Release 8.0.3
A54894-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8(TM)
Getting Started for Windows NT Release 8.0.3 A54894-01 |
|
Oracle8 for Windows NT includes various tools to perform database administration. This chapter describes the preferred tools to perform common database administration tasks.
Specific topics discussed are:
Database tools is a collective term for a number of tools, utilities, and wizards that you can use to perform database administration. Some database tools perform the same tasks, though no one database tool performs all database administration tasks. The following sections indicate which database tools can be used on particular operating systems and the preferred tools to use for common database administration tasks.
This table lists database tools and the operating system on which each can be used.
| Database Tools | Oracle8 Server Software on Windows NT Server | Oracle8 Client Software on Windows NT Client | Oracle8 Client Software on Windows 95 Client |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Oracle8 Utilities |
|
|
|
|
ORADIM801 |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Server Manager (SVRMGR30) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Migration Utility (MIG80) |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Export (EXP80) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Import (IMP80) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
SQL*Loader (SQLLDR80) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Recovery Manager (RMAN80) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Password Utility (ORAPWD80)2 |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
OCOPY80 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows NT Tools |
|
|
|
|
User Manager |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Control Panel |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Oracle Enterprise Manager |
|
|
|
|
Instance Manager |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Data Manager |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Schema Manager |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Security Manager |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Backup Manager |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
SQL Worksheet |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Oracle Assistants (wizards) |
|
|
|
|
Oracle Migration Assistant for Microsoft Access |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Oracle Database Assistant |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Oracle Data Migration Assistant |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Oracle Net8 Assistant |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Oracle Net8 Easy Config |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Oracle INTYPE File Assistant |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
NT Backup Manager3 |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
NT Recovery Manager |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
SQL*Plus |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
This table lists the various database tools you can use to perform common database administration tasks. Oracle Corporation recommends you use the tools listed in the "Preferred Database Tool" column of the table. After choosing a tool to perform a task, go to the section, "Starting Database Tools" in this chapter for instructions on how to start the tool.
| Database Administration Task | Preferred Database Tool | Other Database Tools |
|---|---|---|
|
Create a database |
Oracle Database Assistant |
ORADIM80 and Server Manager together SQL Worksheet |
|
Delete a database |
Oracle Database Assistant |
ORADIM80 and Server Manager together |
|
Delete a database service |
Oracle Database Assistant |
ORADIM80 |
|
Start a database |
Instance Manager1 |
Server Manager, ORADIM80, or SQL Worksheet |
|
Shut down a database |
Instance Manager |
ORADIM80, Server Manager, Control Panel, or SQL Worksheet |
|
Change internal database passwords |
ORAPWD80 |
ORADIM802 |
|
Migrate data |
Oracle Data Migration Assistant |
Migration Utility |
|
Export data |
Data Manager |
Export Utility |
|
Import data |
Data Manager |
Import Utility |
|
Load data |
Data Manager |
SQL*Loader |
|
Back up database |
Backup Manager3 |
RMAN80, NT Backup Manager or OCOPY80 |
|
Recover database |
Backup Manager |
RMAN80, OCOPY80, NT Recovery Manager, or OCOPY80 |
|
Authenticate Database Administrators and users |
Security Manager |
Server Manager, SQL*Plus, or SQL Worksheet |
|
Grant database roles |
Security Manager |
User Manager |
|
Create database objects4 |
Schema Manager |
Server Manager or SQL*Plus |
| 1 Instance Manager
can start up and shut down a database and perform other limited functions.
This tool can not be used to create databases services, or create and delete
databases. 2 ORADIM80 can only set a password when none was previously set. If a password has been previously set, ORADIM80 cannot change it. Also, ORADIM80 can change a password by deleting and recreating the Oracle8 services. 3 Do not back up files while you are shutting down the database, otherwise your backup will be invalid. You can not use an invalid backup to restore files at a later date. 4 See Oracle8 Server Administrator's Guide for guidelines on creating databases objects. In particular, see Appendix A, "Space Estimations for Schema Objects" which provides equations for estimating the space requirements for clusters, nonclustered tables, and indexes. Windows NT uses the same fixed header, transaction header, and row header constants described in that guide. |
This section describes how to start each of the database tools in the following categories:
| Note:
You will frequently be referred back to this section for database tool startup procedures as you use this guide. |
This table describes how to start each Oracle8 Utility, and where to go for further information on using these products.
| Oracle8 Utilities | To Start... | For More Information, See... |
|---|---|---|
|
ORADIM80 |
Enter the following with parameters at the MS-DOS command prompt: C:\> ORADIM80 PARAMETERS To get a complete listing of ORADIM80 parameters, enter a question mark preceded by a dash after the executable name: C:\> ORADIM80 -?Note... If you enter ORADIM80 without parameters at the MS-DOS command prompt, a GUI Instance Manager screen appears. This tool is no longer supported for use on Oracle8 for Windows NT.
|
The section, "Using ORADIM80" in this chapter |
|
Server Manager (Line mode only) |
Enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt: C:\> SVRMGR30
|
|
|
Migration Utility |
Enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt: C:\> MIG80
|
|
|
Export Utility |
Enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt followed by your user name and password. C:\> EXP80 EXP80 runs and prompts you for parameters. To obtain a list of these parameters, enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt: C:\> EXP80 HELP=Y Note... When running the Export utility, the default values for the following parameters under Windows NT are: Note... To export an entire database, you must use the user name SYSTEM. Do not use INTERNAL or SYS. |
|
|
Import Utility |
Enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt followed by your user name and password. C:\> IMP80 IMP80 runs and prompts you for parameters. To obtain a list of these parameters, enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt: C:\> IMP80 HELP=Y Note... When running the Import utility, the default values for the following parameters under Windows NT are: RECORDLENGTH 2 KB |
|
|
SQL*Loader |
Invoke SQL*Loader at the MS-DOS command prompt followed by certain keywords. Enter the following and SQL*Loader displays a Help screen with the available keywords and default values. C:\> SQLLDR80
|
|
|
Recovery Manager (RMAN80) |
Enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt: C:\> RMAN80 PARAMETERS To obtain a list of these parameters enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt: C:\> RMAN80 HELP=Y
|
|
|
Password Utility |
Enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt: C:\> ORAPWD80 FILE=FILENAME PASSWORD=PASSWORD ENTRIES=USERS where:
|
Oracle8 Server Administrator's Guide, which describes how to use the Password utility |
|
OCOPY80 |
Enter the following at the MS-DOS command prompt. C:\> OCOPY80
|
This table describes how to start each Windows NT tool, and where to go for further information on using these products.
| Windows NT Tools | To Start... | For More Information, See... |
|---|---|---|
|
User Manager |
Choose Start>Programs>Administrative Tools>User Manager |
|
|
Control Panel |
Choose Start>Settings>Control Panel |
|
You can start Oracle Enterprise Manager tools:
To start an Oracle Enterprise Manager tool separately:
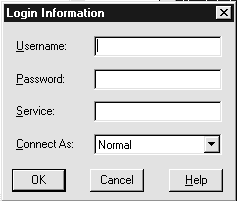
The Login Information dialog box appears:
| Additional
Information:
See the section, "Configuring Oracle Enterprise Manager" in Chapter 6, "Configuration Tasks" for information on configuration tasks you must perform before using Oracle Enterprise Manager and information on how to connect to the Oracle8 database. |
To start an Oracle Enterprise Manager tool from the Console:
The following table describes how to start each Oracle Enterprise Manager tool through the Console, and where to go for further information on using these tools.
| Oracle Enterprise Manager Tools | To Start... | For More Information, See... |
|---|---|---|
|
Instance Manager |
|
The section, "Starting Instance Manager" in Chapter 10, "Managing Instances and Sessions" of Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide |
|
Data Manager |
|
The section, "Starting Data Manager" in Chapter 14, "Managing and Moving Data" of Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide |
|
Schema Manager |
|
The section, "Starting Schema Manager" in Chapter 11, "Managing Schema Objects" of Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide |
|
Security Manager |
|
The section, "Starting Security Manager" in Chapter 9, "Controlling Database Security" of Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide |
|
Backup Manager |
|
The section, "Starting Backup Manager" in Chapter 12, "Managing Backups and Archiving" of Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide |
|
SQL Worksheet |
|
The section, "Overview of the SQL Worksheet" in Chapter 13, "Using the SQL Worksheet" of Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide |
This table describes how to start each assistant, and where to go for further information on using these products.
This table describes how to start NT Backup Manager, and where to go for further information on using this product.
| NT Backup Manager | To Start... | For More Information, See... |
|
NT Backup Manager |
Choose Start>Programs>Oracle for Windows NT>NT Backup Manager |
Online help included with this tool |
This table describes how to start NT Recovery Manager, and where to go for further information on using this product.
| NT Recovery Manager | To Start... | For More Information, See... |
|
NT Recovery Manager |
Choose Start>Programs>Oracle for Windows NT>NT Recovery Manager |
Online help included with this tool |
This table describes how to start SQL*Plus, and where to go for further information on using this product.
| SQL*Plus | To Start... | For More Information, See... |
|
SQL*Plus |
Enter either of the following at the MS-DOS command prompt: C:\> SQLPLUS Starts the line mode version of SQL*Plus or C:\> PLUS80W Starts the GUI version of SQL*Plus or C:\> PLUS80 Starts the line mode version of SQL*Plus Choose Start>Programs>Oracle for Windows NT>SQL*Plus 8.0 Starts the GUI version of SQL*Plus |
|
This section describes the ORADIM80 commands and parameters. Note that each command is preceded by a dash (-).
This section describes Windows NT specific information for using SQL*Loader (SQLLDR80.EXE).
These are the possible values for the Operating System Dependent (OSD) file processing specifications string option, referred to in the "SQL*Loader Control File Reference" chapter of Oracle8 Server Utilities.
| Processing Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
"VAR xxxx" |
Load variable length records. Specify the OSD "VAR recsizehint" in the control file for this option to take effect. The xxxx gives an estimate of the average record size to SQL*Loader so that it can approximate buffer sizes accurately and not waste memory. The default length is eighty characters. The xxxx does not specify how many leading bytes of length are included in each record. It only acts as a hint to SQL*Loader. Each record must always be preceded by five ASCII bytes containing the length of the remainder of the record. For example, a record must look like the following: 00024This is a 24 byte string Any whitespace, carriage returns, or linefeeds at the end of the record are ignored unless specifically included in the byte count in the length field. |
|
"FIX n" |
Fixed record format in which each record is exactly n bytes long. If the record is terminated by a newline character, the newline character must be the nth byte. |
|
""1 |
Stream record format in which each record is terminated by a newline character. The maximum record size is 48 KB. |
| 1 Two double quote
characters with no space in between. |
SQL*Loader includes a direct path option that bypasses Oracle8 redo log and data verification features, thereby decreasing loading time. Use the direct path option with data files known to be error free.
When preparing a SQL*Loader control file (.CTL), you must follow certain syntax and notational conventions. When specifying datatypes in the SQL*Loader control file, note that the default size of native datatypes are specific to Windows NT. You cannot override these defaults in the control file.
| Native Datatypes | Default Field Length |
|---|---|
|
INTEGER |
4 |
|
SMALLINT |
2 |
|
FLOAT |
4 |
|
DOUBLE |
8 |
| Additional
Information:
For a complete list of options and instructions on using SQL*Loader, see Oracle8 Server Utilities. The directory ORACLE_HOME\RDBMS80\LOADER contains a number of examples on the use of SQL*Loader. |
|
Copyright © 1997 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|