| Oracle Network Products Getting Started for Windows Platforms | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Network Products Getting Started for Windows Platforms | Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
Connecting to a Database from a Client Machine
Client workstations and other servers connect to a server's network listener with a service name when logging onto an Oracle7 Server. The appropriate Oracle Protocol Adapter is used automatically when the database alias (or service name) used to request a connection specifies that protocol in the configuration file.
NAMESCTL
NAMESCTL>STATUSIf the STATUS command indicates the Oracle Names Server is running, continue to Step 3. If the Oracle Names Server is not running, continue to Step 2.
NAMESCTL>START
NAMESCTL>QUIT
If the service is not running, continue to Step 3. Otherwise, skip to Step 4.
Command Line To start the listener from the command line:
LSNRCTL
LSNRCTL>STATUS [listener_name]where listener_name is the name of the listener defined in the LISTENER.ORA file. It is not necessary to identify the listener if you are using the default listener, named LISTENER.
If the STATUS command indicates the listener is running, continue to Step 2. If the listener is not running, skip to Step 3.
LSNRCTL>SET PASSWORD password
LSNRCTL>STOP [listener_name]SET PASSWORD is only required if the password is set in the LISTENER.ORA file. The password defaults to ORACLE.
LSNRCTL>START [listener_name]
LSNRCTL>QUIT
If the listener is running, continue to Step 3. If the listener is running, skip to Step 4.
SVRMGR23The SVRMGR> prompt appears:
SVRMGR>CONNECT SYSTEM/MANAGER@service_nameor
SVRMGR>CONNECT SYSTEM/MANAGER@global_dbnameThe service_name is the database alias you defined earlier and the global_dbname is the global database name you defined in the LISTENER.ORA for the Oracle Names Server.
Sever Manager returns a Connected message to the screen.
SVRMGR>EXITExiting Server Manager closes the database connection.

SQL>EXITExiting SQL*Plus closes the database connection.
To stop Oracle Names from the command line:
NAMESCTL
NAMESCTL>STOP
NAMESCTL>QUIT
|
|
Command Line To stop the listener from the command line:
|
|
LSNRCTL
LSNRCTL>SET PASSWORD password
LSNRCTL>STOP [listener_name]where listener_name is the name of the listener defined in the LISTENER.ORA file. It is not necessary to identify the listener if you are using the default listener, named LISTENER.
SET PASSWORD is only required if the password is set in the LISTENER.ORA file. The password is defaulted to ORACLE.
LSNRCTL>QUIT
Windows 16-bit applications are unable to look into a 32-bit environment because the 16-bit applications are expecting to find a real Windows environment with the AUTOEXEC.BAT, WIN.INI, and ORACLE.INI files (rather than the Registry), even though the applications are running on a 32-bit system.
For example, unlike the 32-bit SQL*Plus application, which is able to communicate to the local Oracle7 Server through the native 32-bit internal process communication of the 32-bit operating system, the 16-bit SQL*Plus application requires SQL*Net to break through the "imaginary wall" created when running in 16-bit emulation mode.
Resolving this problem depends upon if you want to connect to a remote or local database
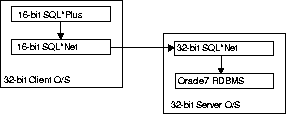
The 16-bit client applications can use the TNSNAMES.ORA and SQLNET.ORA files from the 32-bit ORANT\NETWORK\ADMIN directory as long as the TNS_ADMIN parameter is defined in the ORACLE.INI file and is set to this directory path.
The Bequeath Protocol Adapter, which is automatically installed with the Oracle7 server products, does not use a listener. Therefore, no server configuration is required.
To connect with the Windows NT Authentication Adapter:
SQLNET.AUTHENTICATIONS_SERVICES = (NTS)
SQL>CONNECT SYSTEM/MANAGER;
SQL>CREATE USER ``OPS$[DOMAIN]\USERNAME IDENTIFIED EXTERNALLY'';where [DOMAIN]\USERNAME must be specified in uppercase.
SQL>GRANT role to ``OPS$[DOMAIN]\USERNAME'';
SQL>GRANT CONNECT to ``OPS$[DOMAIN]\USERNAME'';
CONNECT /@service_namewhere service_name identifies the database alias.
|
|
If the ANO NDS Naming Adapter is also used, an NDS user can view the entire network under a single NDS directory tree.
|
|
To connect with the NDS Authentication Adapter:
SQLNET.AUTHENTICATIONS_SERVICES = (NDS)
CONNECT /@service_namewhere service_name identifies the database alias.
SELECT * FROM emp;but you cannot cancel:
SELECT count (*) FROM emp;
Working with Security for the Named Pipes Protocol Adapter
If SQL*Net Server and the Named Pipes Protocol Adapter are on the same machine, you must set up the proper security permission for the Named Pipes Protocol Adapter.
|
Prev Next |
Copyright © 1996 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |