Release 8.1.5
A67789-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i National Language Support Guide Release 8.1.5 A67789-01 |
|
This chapter provides an overview of Oracle NLS support, including:
Oracle's National Language Support (NLS) architecture allows you to store, process, and retrieve data in native languages. It ensures that database utilities and error messages, sort order, date, time, monetary, numeric, and calendar conventions automatically adapt to the native language and locale.
Parameter settings determine the behavior of individual conventions.
Oracle's National Language Support architecture is implemented with the use of the Oracle NLS Runtime Library. The NLS Runtime library provides a comprehensive suite of language-independent functions, which allows for proper text and character processing and language convention manipulations. These functions are for a specific language and locale and are governed by a set of locale-specific data identified and loaded at runtime.
The following diagram illustrates loading locale-specific data at run time. For example, French and Japanese locale data is loaded.
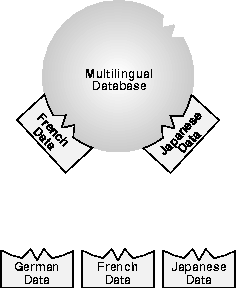
The locale-specific NLS data is stored in a directory specified by the ORA_NLS* environment variable. For each new release, there is a different corresponding ORA_NLS data directory. For Oracle8, release 8.1, the ORA_NLS33 directory is used. For example, on most UNIX platforms, the environment variable ORA_NLS33 should be set to $ORACLE_HOME/ocommon/nls/admin/data.
|
Release |
Environment Variable |
|
7.2 |
ORA_NLS |
|
7.3 |
ORA_NLS32 |
|
8.0, 8.1 |
ORA_NLS33 |
If your system is running in a mixed Oracle environment, you must ensure that the appropriate ORA_NLS* variable is set and that the corresponding NLS data files for that release are available.
A boot file is used to determine the availability of the NLS objects which can be loaded. Oracle supports both system and user boot files. The user boot file gives you the flexibility to tailor what NLS locale objects will be available for the database, thus helping you control memory consumption. Also, new locale-data can be added and some locale-data components can be customized
Oracle8i is implemented using a client/server architecture. The language-dependent operations are controlled by a number of parameters and environment variables on both the client and the server. The server and client may run in the same or different locale, and have the same or different language requirements specified. In the event that the client and server specify different character sets, Oracle8 will handle character set conversion of strings automatically.
Oracle's standard features include language and territory support, as well as support for various date, time, calendar, monetary, numeric and character set formats.
Oracle8i allows users to store, process, and retrieve data in native languages. Table 1-2, "Language Support" lists the languages supported, with an asterisk for languages with translations.
See "Languages" for a complete list of Oracle language names and abbreviations.
Utilities and error messages can be made to appear in the native language.
Oracle8i supports different cultural conventions which are specific to a given geographical location. Local time, date, numeric and monetary conventions are handled. The following territories are supported.
The world's various conventions for hour, day, month, and year can be handled in local formats.
Currency, credit, and debit symbols can be represented in local formats. Radix symbols and thousands separators can be defined by locales.
Gregorian, Japanese Imperial, ROC Official, Thai Buddha, Persian, English Hijrah, and Arabic Hijrah are supported. See "Calendar Systems" for a complete list of calendars.
Oracle8i provides linguistic sorts for culturally accurate sorting.
Oracle supports a large number of single-byte, multi-byte, and fixed-width encoding schemes which are based on national, international, and vendor-specific standards. See "Character Sets" for a complete list of supported character sets.
Oracle allows you to customize character sets and calendars.
User-defined characters are sometimes needed to support special symbols, vendor-specific characters, or characters that represent proper names, historical terms, and so on. Developers can extend an existing character set definition by using the Unicode Private Use Area. See "Customized Character Sets" for further information.
You can define ruler eras for imperial calendars, and deviation days for lunar calendars. See "Customized Calendars" for further information.
NLS parameters can be used to modify the behavior of SQL functions. For instance, SQL functions that deal with time, date, monetary, and numeric formats, as well as sorting and character classification, can change behavior based on different NLS parameters that are implicitly set in the users' environment or explicitly set as a parameter to a function call. See Chapter 4, "SQL Programming", for further information about function calls and see Chapter 2, "Setting Up an NLS Environment", for information about environment parameters.