Release 8.1.5
A67772-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i Administrator's Guide Release 8.1.5 A67772-01 |
|
This chapter describes guidelines for managing schema objects, and includes the following topics:
You should familiarize yourself with the concepts in this chapter before attempting to manage specific schema objects as described in Chapters 13-18.
This section describes the various aspects of managing space in data blocks, and includes the following topics:
You can use the PCTFREE and PCTUSED parameters to make the following changes:
The PCTFREE parameter is used to set the percentage of a block to be reserved for possible updates to rows that already are contained in that block. For example, assume that you specify the following parameter within a CREATE TABLE statement:
PCTFREE 20
This indicates that 20% of each data block used for this table's data segment will be kept free and available for possible updates to the existing rows already within each block. Figure 12-1 illustrates PCTFREE.
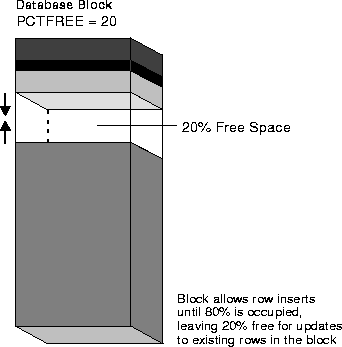
Notice that before the block reaches PCTFREE, the free space of the data block is filled by both the insertion of new rows and by the growth of the data block header.
The default for PCTFREE is 10 percent. You can use any integer between 0 and 99, inclusive, as long as the sum of PCTFREE and PCTUSED does not exceed 100.
A smaller PCTFREE has the following effects:
A small PCTFREE might be suitable, for example, for a segment that is rarely changed.
A larger PCTFREE has the following effects:
A large PCTFREE is suitable, for example, for segments that are frequently updated.
Ensure that you understand the nature of the table or index data before setting PCTFREE. Updates can cause rows to grow. New values might not be the same size as values they replace. If there are many updates in which data values get larger, PCTFREE should be increased. If updates to rows do not affect the total row width, PCTFREE can be low. Your goal is to find a satisfactory trade-off between densely packed data and good update performance.
PCTFREE for NonClustered Tables If the data in the rows of a nonclustered table is likely to increase in size over time, reserve some space for these updates. Otherwise, updated rows are likely to be chained among blocks.
PCTFREE for Clustered Tables The discussion for nonclustered tables also applies to clustered tables. However, if PCTFREE is reached, new rows from any table contained in the same cluster key go into a new data block that is chained to the existing cluster key.
PCTFREE for Indexes You can specify PCTFREE only when initially creating an index.
After a data block becomes full as determined by PCTFREE, Oracle does not consider the block for the insertion of new rows until the percentage of the block being used falls below the parameter PCTUSED. Before this value is achieved, Oracle uses the free space of the data block only for updates to rows already contained in the data block. For example, assume that you specify the following parameter within a CREATE TABLE statement:
PCTUSED 40
In this case, a data block used for this table's data segment is not considered for the insertion of any new rows until the amount of used space in the block falls to 39% or less (assuming that the block's used space has previously reached PCTFREE). Figure 12-2 illustrates this.
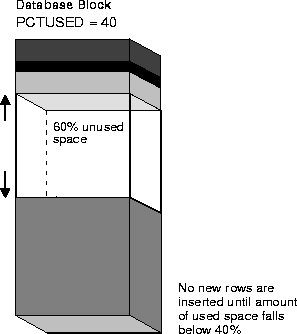
The default value for PCTUSED is 40 percent. After the free space in a data block reaches PCTFREE, no new rows are inserted in that block until the percentage of space used falls below PCTUSED. The percent value is for the block space available for data after overhead is subtracted from total space.
You can specify any integer between 0 and 99 (inclusive) for PCTUSED, as long as the sum of PCTUSED and PCTFREE does not exceed 100.
A smaller PCTUSED has the following effects:
A larger PCTUSED has the following effects:
If you decide not to use the default values for PCTFREE or PCTUSED, keep the following guidelines in mind:
The following examples show how and why specific values for PCTFREE and PCTUSED are specified for tables.
This section describes the storage parameters you can set for various data structures, and includes the following topics:
You can set storage parameters for the following types of logical storage structures:
Every database has default values for storage parameters. You can specify defaults for a tablespace, which override the system defaults to become the defaults for objects created in that tablespace only. Furthermore, you can specify storage settings for each individual object. The storage parameters you can set are:
The size, in bytes, of the first extent allocated when a segment is created.
The size, in bytes, of the next incremental extent to be allocated for a segment. The second extent is equal to the original setting for NEXT. From there forward, NEXT is set to the previous size of NEXT multiplied by (1 + PCTINCREASE/100).
The total number of extents, including the first, that can ever be allocated for the segment.
The total number of extents to be allocated when the segment is created. This allows for a large allocation of space at creation time, even if contiguous space is not available.
The percentage by which each incremental extent grows over the last incremental extent allocated for a segment. If PCTINCREASE is 0, then all incremental extents are the same size. If PCTINCREASE is greater than zero, then each time NEXT is calculated, it grows by PCTINCREASE. PCTINCREASE cannot be negative.
The new NEXT equals 1 + PCTINCREASE/100, multiplied by the size of the last incremental extent (the old NEXT) and rounded up to the next multiple of a block size.
Specifies the number of DML transaction entries for which space should be initially reserved in the data block header. Space is reserved in the headers of all data blocks in the associated data or index segment.
As multiple transactions concurrently access the rows of the same data block, space is allocated for each DML transaction's entry in the block. Once the space reserved by INITRANS is depleted, space for additional transaction entries is allocated out of the free space in a block, if available. Once allocated, this space effectively becomes a permanent part of the block header. The MAXTRANS parameter limits the number of transaction entries that can concurrently use data in a data block. Therefore, you can limit the amount of free space that can be allocated for transaction entries in a data block using MAXTRANS.
The default value is an operating system-specific function of block size, not exceeding 255.
See Also: For specific details about storage parameters, see the Oracle8i SQL Reference.
Some defaults are operating system specific; see your operating system-specific Oracle documentation.
Transaction entry settings for the data blocks allocated for a table, cluster, or index should be set individually for each object based on the following criteria:
For example, if a table is very large and only a small number of users simultaneously access the table, the chances of multiple concurrent transactions requiring access to the same data block is low. Therefore, INITRANS can be set low, especially if space is at a premium in the database.
Alternatively, assume that a table is usually accessed by many users at the same time. In this case, you might consider preallocating transaction entry space by using a high INITRANS (to eliminate the overhead of having to allocate transaction entry space, as required when the object is in use) and allowing a higher MAXTRANS so that no user has to wait to access necessary data blocks.
You can set default storage parameters for each tablespace of a database. Any storage parameter that you do not explicitly set when creating or subsequently altering a segment in a tablespace automatically is set to the corresponding default storage parameter for the tablespace in which the segment resides.
With partitioned tables, you can set default storage parameters at the table level. When creating a new partition of the table, the default storage parameters are inherited from the partitioned table (unless you specify them for the individual partition). If no storage parameters are specified for the partitioned table, then they are inherited from the tablespace.
When specifying MINEXTENTS at the tablespace level, any extent allocated in the tablespace is rounded to a multiple of the number of minimum extents. Basically, the number of extents is a multiple of the number of blocks.
You can set the storage parameters for the data segment of a nonclustered table, snapshot, or snapshot log using the STORAGE clause of the CREATE or ALTER statement for tables, snapshots, or snapshot logs.
In contrast, you set the storage parameters for the data segments of a cluster using the STORAGE clause of the CREATE CLUSTER or ALTER CLUSTER command, rather than the individual CREATE or ALTER commands that put tables and snapshots into the cluster. Storage parameters specified when creating or altering a clustered table or snapshot are ignored. The storage parameters set for the cluster override the table's storage parameters.
Storage parameters for an index segment created for a table index can be set using the STORAGE clause of the CREATE INDEX or ALTER INDEX command. Storage parameters of an index segment created for the index used to enforce a primary key or unique key constraint can be set in the ENABLE clause of the CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE commands or the STORAGE clause of the ALTER INDEX command.
A PCTFREE setting for an index only has an effect when the index is created. You cannot specify PCTUSED for an index segment.
You can set storage parameters for LOB segments using the NOCACHE, NOLOGGING and PCTVERSION LOB storage parameters of the CREATE TABLE statement.
See Also: For a complete list of storage parameters for LOB segments, see the Oracle8i SQL Reference.
You can alter default storage parameters for tablespaces and specific storage parameters for individual segments if the current settings are incorrect. All default storage parameters can be reset for a tablespace. However, changes affect only new objects created in the tablespace, or new extents allocated for a segment.
The INITIAL and MINEXTENTS storage parameters cannot be altered for an existing table, cluster, index, or rollback segment. If only NEXT is altered for a segment, the next incremental extent is the size of the new NEXT, and subsequent extents can grow by PCTINCREASE as usual.
If both NEXT and PCTINCREASE are altered for a segment, the next extent is the new value of NEXT, and from that point forward, NEXT is calculated using PCTINCREASE as usual.
The storage parameters in effect at a given time are determined by the following types of SQL statements, listed in order of precedence:
Any storage parameter specified at the object level overrides the corresponding option set at the tablespace level. When storage parameters are not explicitly set at the object level, they default to those at the tablespace level. When storage parameters are not set at the tablespace level, Oracle system defaults apply. If storage parameters are altered, the new options apply only to the extents not yet allocated.
|
Note: The storage parameters for temporary segments always use the default storage parameters set for the associated tablespace. |
Assume the following statement has been executed:
CREATE TABLE test_storage ( . . . ) STORAGE (INITIAL 100K NEXT 100K MINEXTENTS 2 MAXEXTENTS 5 PCTINCREASE 50);
Also assume that the initialization parameter DB_BLOCK_SIZE is set to 2K. The following table shows how extents are allocated for the TEST_STORAGE table. Also shown is the value for the incremental extent, as can be seen in the NEXT column of the USER_SEGMENTS or DBA_SEGMENTS data dictionary views:
If you change the NEXT or PCTINCREASE storage parameters with an ALTER statement (such as ALTER TABLE), the specified value replaces the current value stored in the data dictionary. For example, the following statement modifies the NEXT storage parameter of the TEST_STORAGE table before the third extent is allocated for the table:
ALTER TABLE test_storage STORAGE (NEXT 500K);
As a result, the third extent is 500K when allocated, the fourth is (500K*1.5)=750K, and so on.
This section describes aspects of deallocating unused space, and includes the following topics:
It is not uncommon to allocate space to a segment, only to find out later that it is not being used. For example, you may set PCTINCREASE to a high value, which could create a large extent that is only partially used. Or you could explicitly overallocate space by issuing the ALTER TABLE...ALLOCATE EXTENT statement. If you find that you have unused or overallocated space, you can release it so that the unused space can be used by other segments.
Prior to deallocation, you can use the DBMS_SPACE package, which contains a procedure (UNUSED_SPACE) that returns information about the position of the high water mark and the amount of unused space in a segment.
Within a segment, the high water mark indicates the amount of used space. You cannot release space below the high water mark (even if there is no data in the space you wish to deallocate). However, if the segment is completely empty, you can release space using the TRUNCATE...DROP STORAGE statement.
The following statements deallocate unused space in a segment (table, index or cluster). The KEEP clause is optional.
ALTER TABLE table DEALLOCATE UNUSED KEEP integer; ALTER INDEX index DEALLOCATE UNUSED KEEP integer; ALTER CLUSTER cluster DEALLOCATE UNUSED KEEP integer;
When you explicitly identify an amount of unused space to KEEP, this space is retained while the remaining unused space is deallocated. If the remaining number of extents becomes smaller than MINEXTENTS, the MINEXTENTS value changes to reflect the new number. If the initial extent becomes smaller, the INITIAL value changes to reflect the new size of the initial extent.
If you do not specify the KEEP clause, all unused space (everything above the high water mark) is deallocated, as long as the size of the initial extent and MINEXTENTS are preserved. Thus, even if the high water mark occurs within the MINEXTENTS boundary, MINEXTENTS remains and the initial extent size is not reduced.
See Also: For details on the syntax and options associated with deallocating unused space, see the Oracle8i SQL Reference.
You can verify that deallocated space is freed by looking at the DBA_FREE_SPACE view. For more information on this view, see the Oracle8i Reference.
This section includes various space deallocation scenarios. Prior to reading it, you should familiarize yourself with the ALTER...DEALLOCATE UNUSED statements in the Oracle8i Reference.
Example 1
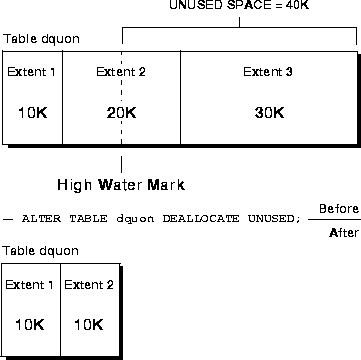
Table DQUON consists of three extents (see Figure 12-3). The first extent is 10K, the second is 20K, and the third is 30K. The high water mark is in the middle of the second extent, and there is 40K of unused space. The following statement deallocates all unused space, leaving table DQUON with two remaining extents. The third extent disappears, and the second extent size is 10K.
ALTER TABLE dquon DEALLOCATE UNUSED;
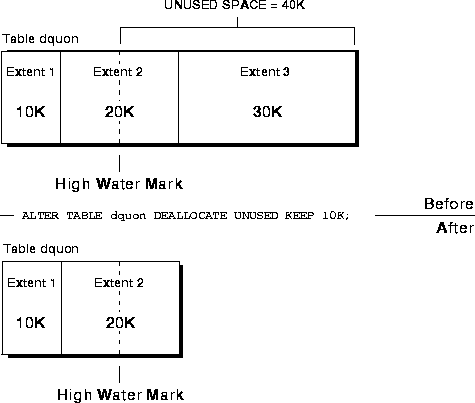
If you deallocate all unused space from DQUON and KEEP 10K (see Figure 12-4), the third extent is deallocated and the second extent remains in tact.
If you deallocate all unused space from DQUON and KEEP 20K, the third extent is cut to 10K, and the size of the second extent remains the same.
ALTER TABLE dquon DEALLOCATE UNUSED KEEP 20K;
Example 2
When you issue the ALTER TABLE DQUON DEALLOCATE UNUSED statement, you completely deallocate the third extent, and the second extent is left with 10K. Note that the size of the next allocated extent defaults to the size of the last completely deallocated extent, which in this example, is 30K. However, if you can explicitly set the size of the next extent using the ALTER...STORAGE [NEXT] statement.
Example 3
To preserve the MINEXTENTS number of extents, DEALLOCATE can retain extents that were originally allocated to an instance (added below the high water mark), while deallocating extents that were originally allocated to the segment.
For example, table DQUON has a MINEXTENTS value of 2. Examples 1 and 2 still yield the same results. However, if the MINEXTENTS value is 3, then the ALTER TABLE DQUON DEALLOCATE UNUSED statement has no effect, while the ALTER TABLE DQUON DEALLOCATE UNUSED KEEP 10K statement removes the third extent and changes the value of MINEXTENTS to 2.
When creating tables and other data structures, you need to know how much space they will require. Each datatype has different space requirements, as described below.
|
DATE Datatype |
The DATE datatype stores point-in-time values such as dates and times. Date data is stored in fixed length fields of seven bytes each. |
|
LONG Datatype |
Columns defined as LONG store variable length character data containing up to two gigabytes of information. LONG data is text data and is appropriately converted when moved between different character sets. LONG data cannot be indexed. Note: You can convert LONG data to LOB data, which has fewer restrictions. For more information see the Oracle8i Application Developer's Guide - Large Objects (LOBs). |
|
|
RAW data can be indexed; LONG RAW data cannot be indexed. |
See Also: For more information about NLS and support for different character sets, see the Oracle8i National Language Support Guide.
For more information about datatypes, see the Oracle8i SQL Reference.
Table 12-2 summarizes important information about each Oracle datatype.