Release 8.1.5
A64686-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i
Java Stored Procedures Developer's Guide Release 8.1.5 A64686-01 |
|
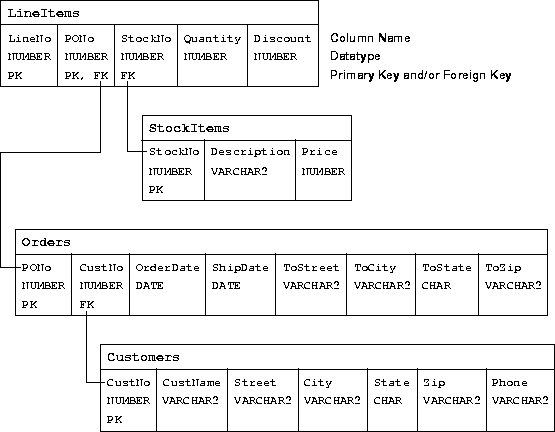
Next, you must devise a schema plan. To do that, you decompose the E-R diagram into the following database tables:
For example, you assign Customer attributes to columns in the table Customers.
Figure 5-3 depicts the relationships between tables. The E-R diagram showed that a line item has a relationship with a purchase order and with a stock item. In the schema plan, you establish these relationships using primary and foreign keys.
A primary key is a column (or combination of columns) whose values uniquely identify each row in a table. A foreign key is a column (or combination of columns) whose values match the primary key in some other table. For example, column PONo in table LineItems is a foreign key matching the primary key in table Orders. Every purchase order number in column LineItems.PONo must also appear in column Orders.PONo.