Release 8.0
A54661_01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Programmer's
Guide to the Oracle Pro*C/C++ Precompiler Release 8.0 A54661_01 |
|
This chapter shows you how to implement dynamic SQL Method 4, which lets your program accept or build dynamic SQL statements that contain a varying number of host variables. Subjects discussed include the following:
Note: For a discussion of dynamic SQL Methods 1, 2, and 3, and an overview of Method 4, see Chapter 13, "Using Dynamic SQL".
Before looking into the requirements of Method 4, you should feel comfortable with the terms select-list item and placeholder. Select-list items are the columns or expressions following the keyword SELECT in a query. For example, the following dynamic query contains three select-list items:
SELECT ename, job, sal + comm FROM emp WHERE deptno = 20
Placeholders are dummy bind variables that hold places in a SQL statement for actual bind variables. You do not declare placeholders, and can name them anything you like.
Placeholders for bind variables are most often used in the SET, VALUES, and WHERE clauses. For example, the following dynamic SQL statements each contain two placeholders:
INSERT INTO emp (empno, deptno) VALUES (:e, :d) DELETE FROM dept WHERE deptno = :num OR loc = :loc
Unlike Methods 1, 2, and 3, dynamic SQL Method 4 lets your program
To add this flexibility to your program, you must give the Oracle runtime library additional information.
The Pro*C/C++ Precompiler generates calls to Oracle for all executable dynamic SQL statements. If a dynamic SQL statement contains no select-list items or placeholders, Oracle needs no additional information to execute the statement. The following DELETE statement falls into this category:
DELETE FROM emp WHERE deptno = 30
However, most dynamic SQL statements contain select-list items or placeholders
for bind variables, as does the following
UPDATE statement:
UPDATE emp SET comm = :c WHERE empno = :e
To execute a dynamic SQL statement that contains placeholders for bind variables or select-list items, Oracle needs information about the program variables that hold the input (bind) values, and that will hold the FETCHed values when a query is executed. The information needed by Oracle is:
All the information Oracle needs about select-list items or placeholders for bind variables, except their values, is stored in a program data structure called the SQL Descriptor Area (SQLDA). The SQLDA struct is defined in the sqlda.h header file.
Descriptions of select-list items are stored in a select descriptor, and descriptions of placeholders for bind variables are stored in a bind descriptor.
The values of select-list items are stored in output variables; the values of bind variables are stored in input variables. You store the addresses of these variables in the select or bind SQLDA so that Oracle knows where to write output values and read input values.
How do values get stored in these data variables? Output values are FETCHed using a cursor, and input values are typically filled in by the program, usually from information entered interactively by the user.
The bind and select descriptors are usually referenced by pointer. A dynamic SQL program should declare a pointer to at least one bind descriptor, and a pointer to at least one select descriptor, in the following way:
EXEC SQL INCLUDE sqlda; SQLDA *bind_dp; SQLDA *select_dp;
You can then use the SQLSQLDAAlloc() function to allocate the descriptor, as follows:
bind_dp = SQLSQLDAAlloc(size, name_length, ind_name_length);
See the section "Allocating a SQLDA" on page 14-5 for detailed information about SQLSQLDAAlloc() and its parameters.
You use the DESCRIBE statement to help obtain the information Oracle needs.
The DESCRIBE SELECT LIST statement examines each select-list item to determine its name, datatype, constraints, length, scale, and precision. It then stores this information in the select SQLDA for your use. For example, you might use select-list names as column headings in a printout. The total number of select-list items is also stored in the SQLDA by DESCRIBE.
The DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES statement examines each placeholder to determine its name and length, then stores this information in an input buffer and bind SQLDA for your use. For example, you might use placeholder names to prompt the user for the values of bind variables.
This section describes the SQLDA data structure in detail. You learn how to declare it, what variables it contains, how to initialize them, and how to use them in your program.
Method 4 is required for dynamic SQL statements that contain an unknown number of select-list items or placeholders for bind variables. To process this kind of dynamic SQL statement, your program must explicitly declare SQLDAs, also called descriptors. Each descriptor is a struct which you must copy or hardcode into your program.
A select descriptor holds descriptions of select-list items, and the addresses of output buffers where the names and values of select-list items are stored.
Note: The "name" of a select-list item can be a column name, a column alias, or the text of an expression such as sal + comm.
A bind descriptor holds descriptions of bind variables and indicator variables, and the addresses of input buffers where the names and values of bind variables and indicator variables are stored.
If your program has more than one active dynamic SQL statement, each statement must have its own SQLDA(s). You can declare any number of SQLDAs with different names. For example, you might declare three select SQLDAs named sel_desc1, sel_desc2, and sel_desc3, so that you can FETCH from three concurrently OPEN cursors. However, non-concurrent cursors can reuse SQLDAs.
To declare a SQLDA, include the sqlda.h header file. The contents of the SQLDA are
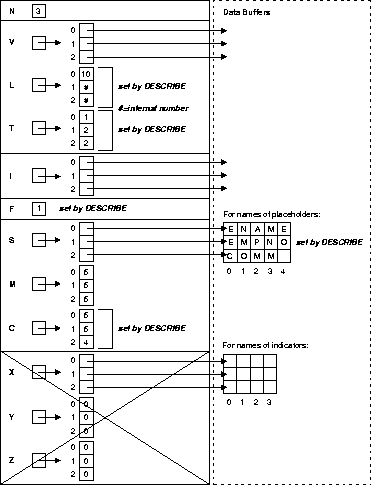
struct SQLDA
{
long N; /* Descriptor size in number of entries */
char **V; Ptr to Arr of addresses of main variables */
long *L; /* Ptr to Arr of lengths of buffers */
short *T; /* Ptr to Arr of types of buffers */
short **I; * Ptr to Arr of addresses of indicator vars */
long F; /* Number of variables found by DESCRIBE */
char **S; /* Ptr to Arr of variable name pointers */
short *M; /* Ptr to Arr of max lengths of var. names */
short *C; * Ptr to Arr of current lengths of var. names */
char **X; /* Ptr to Arr of ind. var. name pointers */
short *Y; /* Ptr to Arr of max lengths of ind. var. names */
short *Z; /* Ptr to Arr of cur lengths of ind. var. names */
};
After declaring a SQLDA, you allocate storage space for it with the sqlaldt() library function, using the syntax
descriptor_name = sqlaldt(max_vars, max_name, max_ind_name);
where:
Besides the descriptor, sqlaldt() allocates data buffers to which descriptor variables point. For more information about sqlaldt(), see "Using the SQLDA Variables" on page 14-7 and "Allocate Storage Space for the Descriptors" on page 14-20.
Figure 14-1 shows whether variables are set by sqlaldt) calls, DESCRIBE commands, FETCH commands, or program assignments.

This section explains the purpose and use of each variable in
the SQLDA.
N specifies the maximum number of select-list items or placeholders that can be DESCRIBEd. Thus, N determines the number of elements in the descriptor arrays.
Before issuing the optional DESCRIBE command, you must set N to the dimension of the descriptor arrays using the sqlaldt() library function. After the DESCRIBE, you must reset N to the actual number of variables DESCRIBEd, which is stored in the F variable.
V is a pointer to an array of addresses of data buffers that store select-list or bind-variable values.
When you allocate the descriptor, sqlaldt() zeros the elements V[0] through V[N - 1] in the array of addresses.
For select descriptors, you must allocate data buffers and set this array before issuing the FETCH command. The statement
EXEC SQL FETCH ... USING DESCRIPTOR ...
directs Oracle to store FETCHed select-list values in the data buffers to which V[0] through V[N - 1] point. Oracle stores the ith select-list value in the data buffer to which V[i] points.
For bind descriptors, you must set this array before issuing the OPEN command. The statement
EXEC SQL OPEN ... USING DESCRIPTOR ...
directs Oracle to execute the dynamic SQL statement using the bind-variable values to which V[0] through V[N - 1] point. Oracle finds the ith bind-variable value in the data buffer to which V[i] points.
L is a pointer to an array of lengths of select-list or bind-variable values stored in data buffers.
For select descriptors, DESCRIBE SELECT LIST sets the array of lengths to the maximum expected for each select-list item. However, you might want to reset some lengths before issuing a FETCH command. FETCH returns at most n characters, where n is the value of L[i] before the FETCH.
The format of the length differs among Oracle datatypes. For CHAR or VARCHAR2 select-list items, DESCRIBE SELECT LIST sets L[i] to the maximum length of the select-list item. For NUMBER select-list items, scale and precision are returned respectively in the low and next-higher bytes of the variable. You can use the library function sqlprc() to extract precision and scale values from L[i]. See the section "Extracting Precision and Scale" on page 14-15.
You must reset L[i] to the required length of the data buffer before the FETCH. For example, when coercing a NUMBER to a C char string, set L[i] to the precision of the number plus two for the sign and decimal point. When coercing a NUMBER to a C float, set L[i] to the length of floats on your system. For more information about the lengths of coerced datatypes, see the section "Converting Data" on page 14-12.
For bind descriptors, you must set the array of lengths before issuing the OPEN command. For example, you can use strlen() to get the lengths of bind-variable character strings entered by the user, then set the appropriate array elements.
Because Oracle accesses a data buffer indirectly, using the address stored in V[i], it does not know the length of the value in that buffer. If you want to change the length Oracle uses for the ith select-list or bind-variable value, reset L[i] to the length you need. Each input or output buffer can have a different length.
T is a pointer to an array of datatype codes of select-list or bind-variable values. These codes determine how Oracle data is converted when stored in the data buffers addressed by elements of the V array. This topic is covered in the section "Converting Data" on page 14-12.
For select descriptors, DESCRIBE SELECT LIST sets the array of datatype codes to the internal datatype (CHAR, NUMBER, or DATE, for example) of the items in the select list.
Before FETCHing, you might want to reset some datatypes because the internal format of Oracle datatypes can be difficult to handle. For display purposes, it is usually a good idea to coerce the datatype of select-list values to VARCHAR2 or STRING. For calculations, you might want to coerce numbers from Oracle to C format. See the section "Coercing Datatypes" on page 14-14.
The high bit of T[i] is set to indicate the null/not null status of the ith select-list item. You must always clear this bit before issuing an OPEN or FETCH command. You use the library function sqlnul() to retrieve the datatype code and clear the null/not null bit. See the section "Handling Null/Not Null Datatypes" on page 14-16.
You should change the Oracle NUMBER internal datatype to an external datatype compatible with that of the C data buffer to which V[i] points.
For bind descriptors, DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES sets the array of datatype codes to zeros. You must set the datatype code stored in each element before issuing the OPEN command. The code represents the external (C) datatype of the data buffer to which V[i] points. Often, bind-variable values are stored in character strings, so the datatype array elements are set to 1 (the VARCHAR2 datatype code). You can also use datatype code 5 (STRING).
To change the datatype of the ith select-list or bind-variable value, reset T[i] to the datatype you want.
I is a pointer to an array of addresses of data buffers that store indicator-variable values.
You must set the elements I[0] through I[N - 1] in the array of addresses.
For select descriptors, you must set the array of addresses before issuing the FETCH command. When Oracle executes the statement
EXEC SQL FETCH ... USING DESCRIPTOR ...
if the ith returned select-list value is null, the indicator-variable value to which I[i] points is set to -1. Otherwise, it is set to zero (the value is not null) or a positive integer (the value was truncated).
For bind descriptors, you must set the array of addresses and associated indicator variables before issuing the OPEN command. When Oracle executes the statement
EXEC SQL OPEN ... USING DESCRIPTOR ...
the data buffer to which I[i] points determines whether the ith bind variable has a null value. If the value of an indicator variable is -1, the value of its associated bind variable is null.
F is the actual number of select-list items or placeholders found
by DESCRIBE.
F is set by DESCRIBE. If F is less than zero, DESCRIBE has found too many select-list items or placeholders for the allocated size of the descriptor. For example, if you set N to 10 but DESCRIBE finds 11 select-list items or placeholders, F is set to -11. This feature lets you dynamically reallocate a larger storage area for select-list items or placeholders if necessary.
S is a pointer to an array of addresses of data buffers that store select-list or placeholder names as they appear in dynamic SQL statements.
You use SQLSQLDAAlloc() to allocate the data buffers and store their addresses in the S array.
DESCRIBE directs Oracle to store the name of the ith select-list item or placeholder in the data buffer to which S[i] points.
M is a pointer to an array of maximum lengths of data buffers that store select-list or placeholder names. The buffers are addressed by elements of the S array.
When you allocate the descriptor, SQLSQLDAAlloc() sets the elements M[0] through M[N - 1] in the array of maximum lengths. When stored in the data buffer to which S[i] points, the ith name is truncated to the length in M[i] if necessary.
C is a pointer to an array of current lengths of select-list or placeholder names.
DESCRIBE sets the elements C[0] through C[N - 1] in the array of current lengths. After a DESCRIBE, the array contains the number of characters in each select-list or placeholder name.
X is a pointer to an array of addresses of data buffers that store indicator-variable names. You can associate indicator-variable values with select-list items and bind variables. However, you can associate indicator-variable names only with bind variables. So, X applies only to bind descriptors.
You use SQLSQLDAAlloc() to allocate the data buffers and store their addresses in the X array.
DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES directs Oracle to store the name of the ith indicator variable in the data buffer to which X[i] points.
Y is a pointer to an array of maximum lengths of data buffers that store indicator-variable names. Like X, Y applies only to bind descriptors.
You use SQLSQLDAAlloc() to set the elements Y[0] through Y[N - 1] in the array of maximum lengths. When stored in the data buffer to which X[i] points, the ith name is truncated to the length in Y[i] if necessary.
Z is a pointer to an array of current lengths of indicator-variable names. Like X and Y, Z applies only to bind descriptors.
DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES sets the elements Z[0] through Z[N - 1] in the array of current lengths. After a DESCRIBE, the array contains the number of characters in each indicator-variable name.
You need a working knowledge of the following subjects to implement dynamic SQL Method 4:
This section provides more detail about the T (datatype) descriptor array. In host programs that use neither datatype equivalencing nor dynamic SQL Method 4, the conversion between Oracle internal and external datatypes is determined at precompile time. By default, the precompiler assigns a specific external datatype to each host variable in the Declare Section. For example, the precompiler assigns the INTEGER external datatype to host variables of type int.
However, Method 4 lets you control data conversion and formatting. You specify conversions by setting datatype codes in the T descriptor array.
Internal datatypes specify the formats used by Oracle to store column values in database tables, as well as the formats used to represent pseudocolumn values.
When you issue a DESCRIBE SELECT LIST command, Oracle returns the internal datatype code for each select-list item to the T descriptor array. For example, the datatype code for the ith select-list item is returned to T[i].
Table 14-1 shows the Oracle internal datatypes and their codes:
| Oracle Internal Datatype | Code |
|---|---|
|
VARCHAR2 |
1 |
|
NUMBER |
2 |
|
LONG |
8 |
|
ROWID |
11 |
|
DATE |
12 |
|
RAW |
23 |
|
LONG RAW |
24 |
|
CHARACTER (or CHAR) |
96 |
|
MLSLABEL |
106 |
External datatypes specify the formats used to store values in input and output host variables.
The DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES command sets the T array of datatype codes to zeros. So, you must reset the codes before issuing the OPEN command. The codes tell Oracle which external datatypes to expect for the various bind variables. For the ith bind variable, reset T[i] to the external datatype you want.
Table 14-2 shows the Oracle external datatypes and their codes, as well as the C datatype normally used with each external datatype.
For more information about the Oracle datatypes and their formats, see Chapter 3, "Developing a Pro*C/C++ Application" in this guide, and Oracle8 Server SQL Reference.
For a select descriptor, DESCRIBE SELECT LIST can return any of the Oracle internal datatypes. Often, as in the case of character data, the internal datatype corresponds exactly to the external datatype you want to use. However, a few internal datatypes map to external datatypes that can be difficult to handle. So, you might want to reset some elements in the T descriptor array. For example, you might want to reset NUMBER values to FLOAT values, which correspond to float values in C. Oracle does any necessary conversion between internal and external datatypes at FETCH time. So, be sure to reset the datatypes after the DESCRIBE SELECT LIST but before the FETCH.
For a bind descriptor, DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES does not return the datatypes of bind variables, only their number and names. Therefore, you must explicitly set the T array of datatype codes to tell Oracle the external datatype of each bind variable. Oracle does any necessary conversion between external and internal datatypes at OPEN time.
When you reset datatype codes in the T descriptor array, you are "coercing datatypes." For example, to coerce the ith select-list value to STRING, you use the following statement:
/* Coerce select-list value to STRING. */ select_des->T[i] = 5;
When coercing a NUMBER select-list value to STRING for display purposes, you must also extract the precision and scale bytes of the value and use them to compute a maximum display length. Then, before the FETCH, you must reset the appropriate element of the L (length) descriptor array to tell Oracle the buffer length to use. See the section "Extracting Precision and Scale" on page 14-15
For example, if DESCRIBE SELECT LIST finds that the ith select-list item is of type NUMBER, and you want to store the returned value in a C variable declared as float, simply set T[i] to 4 and L[i] to the length of floats on your system.
In some cases, the internal datatypes that DESCRIBE SELECT LIST returns might not suit your purposes. Two examples of this are DATE and NUMBER. When you DESCRIBE a DATE select-list item, Oracle returns the datatype code 12 to the T descriptor array. Unless you reset the code before the FETCH, the date value is returned in its 7-byte internal format. To get the date in character format (DD-MON-YY), you can change the datatype code from 12 to 1 (VARCHAR2) or 5 (STRING), and increase the L value from 7 to 9 or 10.
Similarly, when you DESCRIBE a NUMBER select-list item, Oracle returns the datatype code 2 to the T array. Unless you reset the code before the FETCH, the numeric value is returned in its internal format, which is probably not what you want. So, change the code from 2 to 1 (VARCHAR2), 3 (INTEGER), 4 (FLOAT), 5 (STRING) or some other appropriate datatype.
The library function sqlprc() extracts precision and scale. Normally, it is used after the DESCRIBE SELECT LIST, and its first argument is L[i]. You call sqlprc() using the following syntax:
sqlprc(long *length, int *precision, int *scale);
Note: See your platform-specific sqlcpr.h file for the correct prototype for your platform.
where:
When the scale is negative, add its absolute value to the length. For example, a precision of 3 and scale of -2 allow for numbers as large as 99900.
The following example shows how sqlprc() is used to compute maximum display lengths for NUMBER values that will be coerced to STRING:
/* Declare variables for the function call. */
sqlda *select_des; /* pointer to select descriptor */
int prec; /* precision */
int scal; /* scale */
extern void sqlprc(); /* Declare library function. */
/* Extract precision and scale. */
sqlprc( &(select_des->L[i]), &prec, &scal);
/* Allow for maximum size of NUMBER. */
if (prec == 0)
prec = 38;
/* Allow for possible decimal point and sign. */
select_des->L[i] = prec + 2;
/* Allow for negative scale. */
if (scal < 0)
select_des->L[i] += -scal;
Notice that the first argument in this function call points to the ith element in the array of lengths, and that all three parameters are addresses.
The sqlprc() function returns zero as the precision and scale values for certain SQL datatypes. The sqlpr2() function is similar to sqlprc(), having the same argument list, and returning the same values, except in the cases of these SQL datatypes:
| SQL Datatype | Binary Precision | Scale |
|
FLOAT |
126 |
-127 |
|
FLOAT(N) |
N (range is 1 to 126) |
-127 |
|
REAL |
63 |
-127 |
|
DOUBLE PRECISION |
126 |
-127 |
For every select-list column (not expression), DESCRIBE SELECT LIST returns a null/not null indication in the datatype array T of the select descriptor. If the ith select-list column is constrained to be not null, the high-order bit of T[i] is clear; otherwise, it is set.
Before using the datatype in an OPEN or FETCH statement, if the null/not null bit is set, you must clear it. (Never set the bit.)
You can use the library function sqlnul() to find out if a column allows nulls, and to clear the datatype's null/not null bit. You call sqlnul() using the syntax
sqlnul(unsigned short *value_type, unsigned short *type_code, int *null_status);
where:
The following example shows how to use sqlnul():
/* Declare variables for the function call. */
sqlda *select_des; /* pointer to select descriptor */
unsigned short dtype; /* datatype without null bit */
int nullok; /* 1 = null, 0 = not null */
extern void sqlnul(); /* Declare library function. */
/* Find out whether column is not null. */
sqlnul(&select_des->T[i], &dtype, &nullok);
if (nullok)
{
/* Nulls are allowed. */
...
/* Clear the null/not null bit. */
sqlnul(&(select_des->T[i]), &(select_des->T[i]), &nullok);
}
Notice that the first and second arguments in the second call to the sqlnul() function point to the ith element in the array of datatypes, and that all three parameters are addresses.
Method 4 can be used to process any dynamic SQL statement. In the coming example, a query is processed so you can see how both input and output host variables are handled.
To process the dynamic query, our example program takes the following steps:
Note: Some of these steps are unnecessary if the dynamic SQL statement contains a known number of select-list items or placeholders.
This section discusses each step in detail. Also, at the end of this chapter is a Commented, full-length program illustrating Method 4.
With Method 4, you use the following sequence of embedded SQL statements:
EXEC SQL PREPARE statement_name
FROM { :host_string | string_literal };
EXEC SQL DECLARE cursor_name CURSOR FOR statement_name;
EXEC SQL DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES FOR statement_name
INTO bind_descriptor_name;
EXEC SQL OPEN cursor_name
[USING DESCRIPTOR bind_descriptor_name];
EXEC SQL DESCRIBE [SELECT LIST FOR] statement_name
INTO select_descriptor_name;
EXEC SQL FETCH cursor_name
USING DESCRIPTOR select_descriptor_name;
EXEC SQL CLOSE cursor_name;
If the number of select-list items in a dynamic query is known, you can omit DESCRIBE SELECT LIST and use the following Method 3 FETCH statement:
EXEC SQL FETCH cursor_name INTO host_variable_list;
Or, if the number of placeholders for bind variables in a dynamic SQL statement is known, you can omit DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES and use the following Method 3 OPEN statement:
EXEC SQL OPEN cursor_name [USING host_variable_list];
Next, you see how these statements allow your host program to accept and process a dynamic SQL statement using descriptors.
Note: Several figures accompany the following discussion. To avoid cluttering the figures, it was necessary to do the following:
Your program needs a host variable to store the text of the dynamic SQL statement. The host variable (select_stmt in our example) must be declared as a character string.
...
int emp_number;
VARCHAR emp_name[10];
VARCHAR select_stmt[120];
float bonus;
In our example, instead of hardcoding the SQLDA data structure, you use INCLUDE to copy it into your program, as follows:
EXEC SQL INCLUDE sqlda;
Then, because the query might contain an unknown number of select-list items or placeholders for bind variables, you declare pointers to select and bind descriptors, as follows:
sqlda *select_des; sqlda *bind_des;
Recall that you allocate storage space for a descriptor with the SQLSQLDAAlloc() library function. The syntax, using ANSI C notation, is:
SQLDA *SQLSQLDAAlloc(int max_vars, size_t max_name, size_t max_ind_name);
The SQLSQLDAAlloc() function allocates the descriptor structure and the arrays addressed by the pointer variables V, L, T, and I.
If max_name is non-zero, arrays addressed by the pointer variables S, M, and C are allocated. If max_ind_name is non-zero, arrays addressed by the pointer variables X, Y, and Z are allocated. No space is allocated if max_name and max_ind_name are zero.
If SQLSQLDAAlloc() succeeds, it returns a pointer to the structure. If SQLSQLDAAlloc() fails, it returns a zero.
In our example, you allocate select and bind descriptors, as follows:
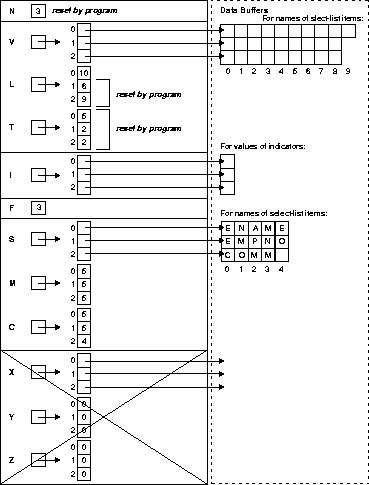
select_des = SQLSQLDAAlloc(3, (size_t) 5, (size_t) 0); bind_des = SQLSQLDAAlloc(3, (size_t) 5, (size_t) 4);
For select descriptors, always set max_ind_name to zero so that no space is allocated for the array addressed by X.
Next, you set the maximum number of select-list items or placeholders that can be DESCRIBEd, as follows:
select_des->N = 3; bind_des->N = 3;
Figure 14-2 and Figure 14-3 represent the resulting descriptors. Note: In the select descriptor (Figure 14-2), the section for indicator-variable names is crossed out to show that it is not used.
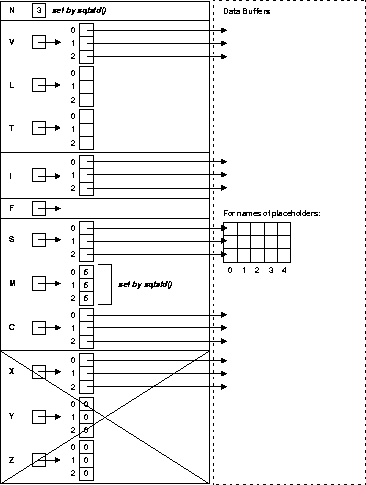
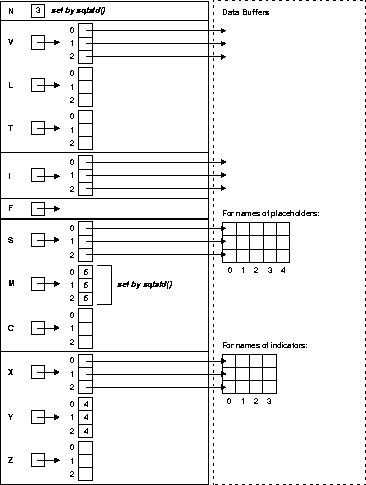
Continuing our example, you prompt the user for a SQL statement, then store the input string in select_stmt, as follows:
printf("\n\nEnter SQL statement: ");
gets(select_stmt.arr);
select_stmt.len = strlen(select_stmt.arr);
We assume the user entered the following string:
"SELECT ename, empno, comm FROM emp WHERE comm < :bonus"
PREPARE parses the SQL statement and gives it a name. In our example, PREPARE parses the host string select_stmt and gives it the name sql_stmt, as follows:
EXEC SQL PREPARE sql_stmt FROM :select_stmt;
DECLARE CURSOR defines a cursor by giving it a name and associating it with a specific SELECT statement.
To declare a cursor for static queries, you use the following syntax:
EXEC SQL DECLARE cursor_name CURSOR FOR SELECT ...
To declare a cursor for dynamic queries, the statement name given to the dynamic query by PREPARE is substituted for the static query. In our example, DECLARE CURSOR defines a cursor named emp_cursor and associates it with sql_stmt, as follows:
EXEC SQL DECLARE emp_cursor CURSOR FOR sql_stmt;
Note: You must declare a cursor for all dynamic SQL statements, not just queries. With non-queries, OPENing the cursor executes the dynamic SQL statement.
DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES puts descriptions of placeholders into a bind descriptor. In our example, DESCRIBE readies bind_des, as follows:
EXEC SQL DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES FOR sql_stmt INTO bind_des;
Note that bind_des must not be prefixed with a colon.
The DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES statement must follow the PREPARE statement but precede the OPEN statement.
Figure 14-4 shows the bind descriptor in our example after the DESCRIBE. Notice that DESCRIBE has set F to the actual number of placeholders found in the processed SQL statement.
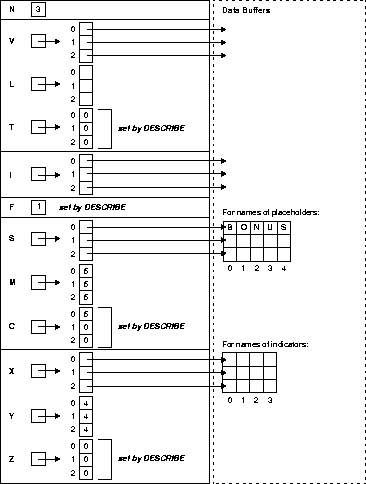
Next, you must reset the maximum number of placeholders to the number actually found by DESCRIBE, as follows:
bind_des->N = bind_des->F;
Your program must get values for the bind variables found in the SQL statement, and allocate memory for them. How the program gets the values is up to you. For example, they can be hardcoded, read from a file, or entered interactively.
In our example, a value must be assigned to the bind variable that replaces the placeholder bonus in the query WHERE clause. So, you choose to prompt the user for the value, then process it as follows:
for (i = 0; i < bind_des->F; i++)
{
printf("\nEnter value of bind variable %.*s:\n? ",
(int) bind_des->C[i], bind_des->S[i]);
gets(hostval);
/* Set length of value. */
bind_des->L[i] = strlen(hostval);
/* Allocate storage for value and null terminator. */
bind_des->V[i] = malloc(bind_des->L[i] + 1);
/* Allocate storage for indicator value. */
bind_des->I[i] = (unsigned short *) malloc(sizeof(short));
/* Store value in bind descriptor. */
strcpy(bind_des->V[i], hostval);
/* Set value of indicator variable. */
*(bind_des->I[i]) = 0; /* or -1 if "null" is the value */
/* Set datatype to STRING. */
bind_des->T[i] = 5;
}
Assuming that the user supplied a value of 625 for bonus, Figure 14-5 shows the resulting bind descriptor. Notice that the value is null-terminated.
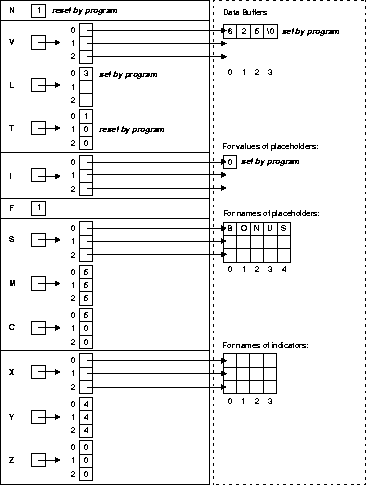
The OPEN statement used for dynamic queries is like that used for static queries except that the cursor is associated with a bind descriptor. Values determined at run time and stored in buffers addressed by elements of the bind descriptor arrays are used to evaluate the SQL statement. With queries, the values are also used to identify the active set.
In our example, OPEN associates emp_cursor with bind_des, as follows:
EXEC SQL OPEN emp_cursor USING DESCRIPTOR bind_des;
Remember, bind_des must not be prefixed with a colon.
Then, OPEN executes the SQL statement. With queries, OPEN also identifies the active set and positions the cursor at the first row.
If the dynamic SQL statement is a query, the DESCRIBE SELECT LIST statement must follow the OPEN statement but precede the FETCH statement.
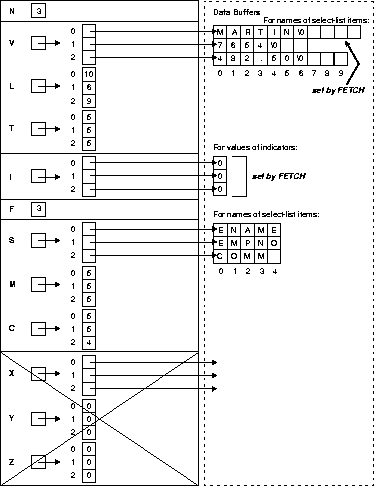
DESCRIBE SELECT LIST puts descriptions of select-list items in a select descriptor. In our example, DESCRIBE readies select_des, as follows:
EXEC SQL DESCRIBE SELECT LIST FOR sql_stmt INTO select_des;
Accessing the Oracle data dictionary, DESCRIBE sets the length and datatype of each select-list value.
Figure 14-6 shows the select descriptor in our example after the DESCRIBE. Notice that DESCRIBE has set F to the actual number of items found in the query select list. If the SQL statement is not a query, F is set to zero.
Also notice that the NUMBER lengths are not usable yet. For columns defined as NUMBER, you must use the library function sqlprc() to extract precision and scale. See "Coercing Datatypes" on page 14-14.
Next, you must reset the maximum number of select-list items to the number actually found by DESCRIBE, as follows:
select_des->N = select_des->F;
In our example, before FETCHing the select-list values, you allocate storage space for them using the library function malloc(). You also reset some elements in the length and datatype arrays for display purposes.
for (i=0; i<select_des->F; i++)
{
/* Clear null bit. */
sqlnul(&(select_des->T[i], &(select_des->T[i], &nullok)));
/* Reset length if necessary. */
switch(select_des->T[i])
{
case 1: break;
case 2: sqlprc(&select_des->L[i], &prec, &scal);
if (prec == 0) prec = 40;
select_des->L[i] = prec + 2;
if (scal < 0) select_des->L[i] += -scal;
break;
case 8: select_des->L[i] = 240;
break;
case 11: select_des->L[i] = 18;
break;
case 12: select_des->L[i] = 9;
break;
case 23: break;
case 24: select_des->L[i] = 240;
break;
}
/* Allocate storage for select-list value. */
select_des->V[i] = malloc(select_des->L[i+1]);
/* Allocate storage for indicator value. */
select_des->I[i] = (short *)malloc(sizeof(short *));
/* Coerce all datatypes except LONG RAW to STRING. */
if (select_des->T[i] != 24) select_des->T[i] = 5;
}
Figure 14-7 shows the resulting select descriptor. Notice that the NUMBER lengths are now usable and that all the datatypes are STRING. The lengths in L[1] and L[2] are 6 and 9 because we increased the DESCRIBEd lengths of 4 and 7 by 2 to allow for a possible sign and decimal point.
FETCH returns a row from the active set, stores select-list values in the data buffers, and advances the cursor to the next row in the active set. If there are no more rows, FETCH sets sqlca.sqlcode to the "no data found" Oracle error code. In our example, FETCH returns the values of columns ENAME, EMPNO, and COMM to select_des, as follows:
EXEC SQL FETCH emp_cursor USING DESCRIPTOR select_des;
Figure 14-8 shows the select descriptor in our example after the FETCH. Notice that Oracle has stored the select-list and indicator values in the data buffers addressed by the elements of V and I.
For output buffers of datatype 1, Oracle, using the lengths stored in
the L array, left-justifies CHAR or VARCHAR2 data and right-justifies
NUMBER data. For output buffer of type 5 (STRING), Oracle left-justifies
and null terminates CHAR, VARCHAR2, and
NUMBER data.
The value `MARTIN' was retrieved from a VARCHAR2(10) column in the EMP table. Using the length in L[0], Oracle left-justifies the value in a 10-byte field, filling the buffer.
The value 7654 was retrieved from a NUMBER(4) column and coerced to '7654'. However, the length in L[1] was increased by 2 to allow for a possible sign and decimal point. So, Oracle left-justifies and null terminates the value in a 6-byte field.
The value 482.50 was retrieved from a NUMBER(7,2) column and coerced to '482.50'. Again, the length in L[2] was increased by 2. So, Oracle left-justifies and null terminates the value in a 9-byte field.
After the FETCH, your program can process the returned values. In
our example, values for columns ENAME, EMPNO, and COMM
are processed.
You use the free() library function to deallocate the storage space allocated by malloc(). The syntax is as follows:
free(char *pointer);
In our example, you deallocate storage space for the values of the select-list items, bind variables, and indicator variables, as follows:
for (i = 0; i < select_des->F; i++) /* for select descriptor */
{
free(select_des->V[i]);
free(select_des->I[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < bind_des->F; i++) /* for bind descriptor */
{
free(bind_des->V[i]);
free(bind_des->I[i]);
}
You deallocate storage space for the descriptors themselves with the sqlclu() library function, using the following syntax:
sqlclu(descriptor_name);
The descriptor must have been allocated using SQLSQLDAAlloc(). Otherwise, the results are unpredictable.
In our example, you deallocate storage space for the select and bind descriptors as follows:
sqlclu(select_des); sqlclu(bind_des);
CLOSE disables the cursor. In our example, CLOSE disables emp_cursor as follows:
EXEC SQL CLOSE emp_cursor;
To use input or output host arrays with Method 4, you must use the optional FOR clause to tell Oracle the size of your host array. For more information about the FOR clause, see Chapter 12, "Using Host Arrays".
You must set descriptor entries for the ith select-list item or bind variable using the syntax
V[i] = array_address; L[i] = element_size;
where array_address is the address of the host array, and element_size is the size of one array element.
Then, you must use a FOR clause in the EXECUTE or FETCH statement (whichever is appropriate) to tell Oracle the number of array elements you want to process. This procedure is necessary because Oracle has no other way of knowing the size of your host array.
In the complete program example below, three input host arrays are used to INSERT rows into the EMP table. Note that EXECUTE can be used for Data Manipulation Language statements other than queries with Method 4.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sqlca.h>
#include <sqlda.h>
#define NAME_SIZE 10
#define ARRAY_SIZE 5
/* connect string */
char *username = "scott/tiger";
char *sql_stmt =
"INSERT INTO emp (empno, ename, deptno) VALUES (:e, :n, :d)";
int array_size = ARRAY_SIZE; /* must have a host variable too */
SQLDA *binda;
char names[ARRAY_SIZE][NAME_SIZE];
int numbers[ARRAY_SIZE], depts[ARRAY_SIZE];
extern SQLDA *SQLSQLDAAlloc();
main()
{
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLERROR GOTO sql_error;
/* Connect */
EXEC SQL CONNECT :username;
printf("Connected.\n");
/* Allocate the descriptors and set the N component.
This must be done before the DESCRIBE. */
binda = SQLSQLDAAlloc(3, ARRAY_SIZE, 0);
binda->N = 3;
/* Prepare and describe the SQL statement. */
EXEC SQL PREPARE stmt FROM :sql_stmt;
EXEC SQL DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES FOR stmt INTO binda;
/* Initialize the descriptors. */
binda->V[0] = (char *) numbers;
binda->L[0] = (long) sizeof (int);
binda->T[0] = 3;
binda->I[0] = 0;
binda->V[1] = (char *) names;
binda->L[1] = (long) NAME_SIZE;
binda->T[1] = 1;
binda->I[1] = 0;
binda->V[2] = (char *) depts;
binda->L[2] = (long) sizeof (int);
binda->T[2] = 3;
binda->I[2] = 0;
/* Initialize the data buffers. */
strcpy(&names[0] [0], "ALLISON");
numbers[0] = 1014;
depts[0] = 30;
strcpy(&names[1] [0], "TRUSDALE");
numbers[1] = 1015;
depts[1] = 30;
strcpy(&names[2] [0], "FRAZIER");
numbers[2] = 1016;
depts[2] = 30;
strcpy(&names[3] [0], "CARUSO");
numbers[3] = 1017;
depts[3] = 30;
strcpy(&names[4] [0], "WESTON");
numbers[4] = 1018;
depts[4] = 30;
/* Do the INSERT. */
printf("Adding to the Sales force...\n");
EXEC SQL FOR :array_size
EXECUTE stmt USING DESCRIPTOR binda;
/* Print rows-processed count. */
printf("%d rows inserted.\n\n", sqlca.sqlerrd[2]);
EXEC SQL COMMIT RELEASE;
exit(0);
sql_error:
/* Print Oracle error message. */
printf("\n%.70s", sqlca.sqlerrm.sqlerrmc);
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLERROR CONTINUE;
EXEC SQL ROLLBACK RELEASE;
exit(1);
}
This program shows the basic steps required to use dynamic SQL with Method 4. After connecting to Oracle, the program allocates memory for the descriptors using SQLSQLDAAlloc(), prompts the user for a SQL statement, PREPAREs the statement, DECLAREs a cursor, checks for any bind variables using DESCRIBE BIND, OPENs the cursor, and DESCRIBEs any select-list items. If the input SQL statement is a query, the program FETCHes each row of data, then CLOSEs the cursor. This program is available on-line in the demo directory, in the file sample10.pc.
/****************************************************************
Sample Program 10: Dynamic SQL Method 4
This program connects you to ORACLE using your username and
password, then prompts you for a SQL statement. You can enter
any legal SQL statement.
Use regular SQL syntax, not embedded SQL. Your statement will
be processed. If it is a query, the rows fetched are
displayed. You can enter multi-line statements. The limit is
1023 bytes.
This sample program only processes up to MAX_ITEMS bind
variables and MAX_ITEMS select-list items. MAX_ITEMS is
#defined to be 40.
****************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
/* Maximum number of select-list items or bind variables. */
#define MAX_ITEMS 40
/* Maximum lengths of the _names_ of the
select-list items or indicator variables. */
#define MAX_VNAME_LEN 30
#define MAX_INAME_LEN 30
#ifndef NULL
#define NULL 0
#endif
char *dml_commands[] = {"SELECT", "select", "INSERT", "insert",
"UPDATE", "update", "DELETE", "delete"};
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION;
char dyn_statement[1024];
EXEC SQL VAR dyn_statement IS STRING(1024);
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION;
EXEC SQL INCLUDE sqlca;
EXEC SQL INCLUDE sqlda;
SQLDA *bind_dp;
SQLDA *select_dp;
extern SQLDA *SQLSQLDAAlloc();
extern void sqlnul();
/* Define a buffer to hold longjmp state info. */
jmp_buf jmp_continue;
/* A global flag for the error routine. */
int parse_flag = 0;
main()
{
int oracle_connect();
int alloc_descriptors();
int get_dyn_statement();
int set_bind_variables();
int process_select_list();
int i;
/* Connect to the database. */
if (oracle_connect() != 0)
exit(1);
/* Allocate memory for the select and bind descriptors. */
if (alloc_descriptors(MAX_ITEMS,
MAX_VNAME_LEN, MAX_INAME_LEN) != 0)
exit(1);
/* Process SQL statements. */
for (;;)
{
i = setjmp(jmp_continue);
/* Get the statement. Break on "exit". */
if (get_dyn_statement() != 0)
break;
/* Prepare the statement and declare a cursor. */
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLERROR DO sql_error();
parse_flag = 1; /* Set a flag for sql_error(). */
EXEC SQL PREPARE S FROM :dyn_statement;
parse_flag = 0; /* Unset the flag. */
EXEC SQL DECLARE C CURSOR FOR S;
/* Set the bind variables for any placeholders in the
SQL statement. */
set_bind_variables();
/* Open the cursor and execute the statement.
* If the statement is not a query (SELECT), the
* statement processing is completed after the
* OPEN.
*/
EXEC SQL OPEN C USING DESCRIPTOR bind_dp;
/* Call the function that processes the select-list.
* If the statement is not a query, this function
* just returns, doing nothing.
*/
process_select_list();
/* Tell user how many rows processed. */
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if (strncmp(dyn_statement, dml_commands[i], 6) == 0)
{
printf("\n\n%d row%c processed.\n",
sqlca.sqlerrd[2],
sqlca.sqlerrd[2] == 1 ? '\0' : 's');
break;
}
}
} /* end of for(;;) statement-processing loop */
/* When done, free the memory allocated for
pointers in the bind and select descriptors. */
for (i = 0; i < MAX_ITEMS; i++)
{
if (bind_dp->V[i] != (char *) 0)
free(bind_dp->V[i]);
free(bind_dp->I[i]); /* MAX_ITEMS were allocated. */
if (select_dp->V[i] != (char *) 0)
free(select_dp->V[i]);
free(select_dp->I[i]); /* MAX_ITEMS were allocated. */
}
/* Free space used by the descriptors themselves. */
sqlclu(bind_dp);
sqlclu(select_dp);
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLERROR CONTINUE;
/* Close the cursor. */
EXEC SQL CLOSE C;
EXEC SQL COMMIT WORK RELEASE;
puts("\nHave a good day!\n");
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLERROR DO sql_error();
return;
}
oracle_connect()
{
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION;
VARCHAR username[128];
VARCHAR password[32];
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION;
printf("\nusername: ");
fgets((char *) username.arr, sizeof username.arr, stdin);
fflush(stdin);
username.arr[strlen((char *) username.arr)-1] = '\0';
username.len = strlen((char *) username.arr);
printf("password: ");
fgets((char *) password.arr, sizeof password.arr, stdin);
fflush(stdin);
password.arr[strlen((char *) password.arr) - 1] = '\0';
password.len = strlen((char *) password.arr);
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLERROR GOTO connect_error;
EXEC SQL CONNECT :username IDENTIFIED BY :password;
printf("\nConnected to ORACLE as user %s.\n", username.arr);
return 0;
connect_error:
fprintf(stderr,
"Cannot connect to ORACLE as user %s\n",
username.arr);
return -1;
}
/*
* Allocate the BIND and SELECT descriptors using SQLSQLDAAlloc().
* Also allocate the pointers to indicator variables
* in each descriptor. The pointers to the actual bind
* variables and the select-list items are realloc'ed in
* the set_bind_variables() or process_select_list()
* routines. This routine allocates 1 byte for select_dp->V[i]
* and bind_dp->V[i], so the realloc will work correctly.
*/
alloc_descriptors(size, max_vname_len, max_iname_len)
int size;
int max_vname_len;
int max_iname_len;
{
int i;
/*
* The first SQLSQLDAAlloc parameter determines the maximum number
* of array elements in each variable in the descriptor. In
* other words, it determines the maximum number of bind
* variables or select-list items in the SQL statement.
*
* The second parameter determines the maximum length of
* strings used to hold the names of select-list items
* or placeholders. The maximum length of column
* names in ORACLE is 30, but you can allocate more or less
* as needed.
*
* The third parameter determines the maximum length of
* strings used to hold the names of any indicator
* variables. To follow ORACLE standards, the maximum
* length of these should be 30. But, you can allocate
* more or less as needed.
*/
if ((bind_dp =
SQLSQLDAAlloc(size,
max_vname_len, max_iname_len)) == (SQLDA *) 0)
{
fprintf(stderr,
"Cannot allocate memory for bind descriptor.");
return -1; /* Have to exit in this case. */
}
if ((select_dp =
SQLSQLDAAlloc (size,
max_vname_len, max_iname_len)) == (SQLDA *) 0)
{
fprintf(stderr,
"Cannot allocate memory for select descriptor.");
return -1;
}
select_dp->N = MAX_ITEMS;
/* Allocate the pointers to the indicator variables, and the
actual data. */
for (i = 0; i < MAX_ITEMS; i++) {
bind_dp->I[i] = (short *) malloc(sizeof (short));
select_dp->I[i] = (short *) malloc(sizeof(short));
bind_dp->V[i] = (char *) malloc(1);
select_dp->V[i] = (char *) malloc(1);
}
return 0;
}
get_dyn_statement()
{
char *cp, linebuf[256];
int iter, plsql;
int help();
for (plsql = 0, iter = 1; ;)
{
if (iter == 1)
{
printf("\nSQL> ");
dyn_statement[0] = '\0';
}
fgets(linebuf, sizeof linebuf, stdin);
fflush(stdin);
cp = strrchr(linebuf, '\n');
if (cp && cp != linebuf)
*cp = ' ';
else if (cp == linebuf)
continue;
if ((strncmp(linebuf, "EXIT", 4) == 0) ||
(strncmp(linebuf, "exit", 4) == 0))
{
return -1;
}
else if (linebuf[0] == '?' ||
(strncmp(linebuf, "HELP", 4) == 0) ||
(strncmp(linebuf, "help", 4) == 0))
{
help();
iter = 1;
continue;
}
if (strstr(linebuf, "BEGIN") ||
(strstr(linebuf, "begin")))
{
plsql = 1;
}
strcat(dyn_statement, linebuf);
if ((plsql && (cp = strrchr(dyn_statement, '/'))) ||
(!plsql && (cp = strrchr(dyn_statement, ';'))))
{
*cp = '\0';
break;
}
else
{
iter++;
printf("%3d ", iter);
}
}
return 0;
}
set_bind_variables()
{
int i, n;
char bind_var[64];
/* Describe any bind variables (input host variables) */
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLERROR DO sql_error();
bind_dp->N = MAX_ITEMS; /* Init. count of array elements. */
EXEC SQL DESCRIBE BIND VARIABLES FOR S INTO bind_dp;
/* If F is negative, there were more bind variables
than originally allocated by SQLSQLDAAlloc(). */
if (bind_dp->F < 0)
{
printf
("\nToo many bind variables (%d), maximum is %d.\n",
-bind_dp->F, MAX_ITEMS);
return;
}
/* Set the maximum number of array elements in the
descriptor to the number found. */
bind_dp->N = bind_dp->F;
/* Get the value of each bind variable as a
* character string.
*
* C[i] contains the length of the bind variable
* name used in the SQL statement.
* S[i] contains the actual name of the bind variable
* used in the SQL statement.
*
* L[i] will contain the length of the data value
* entered.
*
* V[i] will contain the address of the data value
* entered.
*
* T[i] is always set to 1 because in this sample program
* data values for all bind variables are entered
* as character strings.
* ORACLE converts to the table value from CHAR.
*
* I[i] will point to the indicator value, which is
* set to -1 when the bind variable value is "null".
*/
for (i = 0; i < bind_dp->F; i++)
{
printf ("\nEnter value for bind variable %.*s: ",
(int)bind_dp->C[i], bind_dp->S[i]);
fgets(bind_var, sizeof bind_var, stdin);
/* Get length and remove the new line character. */
n = strlen(bind_var) - 1;
/* Set it in the descriptor. */
bind_dp->L[i] = n;
/* (re-)allocate the buffer for the value.
SQLSQLDAAlloc() reserves a pointer location for
V[i] but does not allocate the full space for
the pointer. */
bind_dp->V[i] = (char *) realloc(bind_dp->V[i],
(bind_dp->L[i] + 1));
/* And copy it in. */
strncpy(bind_dp->V[i], bind_var, n);
/* Set the indicator variable's value. */
if ((strncmp(bind_dp->V[i], "NULL", 4) == 0) ||
(strncmp(bind_dp->V[i], "null", 4) == 0))
*bind_dp->I[i] = -1;
else
*bind_dp->I[i] = 0;
/* Set the bind datatype to 1 for CHAR. */
bind_dp->T[i] = 1;
}
}
process_select_list()
{
int i, null_ok, precision, scale;
if ((strncmp(dyn_statement, "SELECT", 6) != 0) &&
(strncmp(dyn_statement, "select", 6) != 0))
{
select_dp->F = 0;
return;
}
/* If the SQL statement is a SELECT, describe the
select-list items. The DESCRIBE function returns
their names, datatypes, lengths (including precision
and scale), and NULL/NOT NULL statuses. */
select_dp->N = MAX_ITEMS;
EXEC SQL DESCRIBE SELECT LIST FOR S INTO select_dp;
/* If F is negative, there were more select-list
items than originally allocated by SQLSQLDAAlloc(). */
if (select_dp->F < 0)
{
printf
("\nToo many select-list items (%d), maximum is %d\n",
-(select_dp->F), MAX_ITEMS);
return;
}
/* Set the maximum number of array elements in the
descriptor to the number found. */
select_dp->N = select_dp->F;
/* Allocate storage for each select-list item.
sqlprc() is used to extract precision and scale
from the length (select_dp->L[i]).
sqlnul() is used to reset the high-order bit of
the datatype and to check whether the column
is NOT NULL.
CHAR datatypes have length, but zero precision and
scale. The length is defined at CREATE time.
NUMBER datatypes have precision and scale only if
defined at CREATE time. If the column
definition was just NUMBER, the precision
and scale are zero, and you must allocate
the required maximum length.
DATE datatypes return a length of 7 if the default
format is used. This should be increased to
9 to store the actual date character string.
If you use the TO_CHAR function, the maximum
length could be 75, but will probably be less
(you can see the effects of this in SQL*Plus).
ROWID datatype always returns a fixed length of 18 if
coerced to CHAR.
LONG and
LONG RAW datatypes return a length of 0 (zero),
so you need to set a maximum. In this example,
it is 240 characters.
*/
printf ("\n");
for (i = 0; i < select_dp->F; i++)
{
/* Turn off high-order bit of datatype (in this example,
it does not matter if the column is NOT NULL). */
sqlnul (&(select_dp->T[i]),
&(select_dp->T[i]), &null_ok);
switch (select_dp->T[i])
{
case 1 : /* CHAR datatype: no change in length
needed, except possibly for TO_CHAR
conversions (not handled here). */
break;
case 2 : /* NUMBER datatype: use sqlprc() to
extract precision and scale. */
sqlprc (&(select_dp->L[i]), &precision, &scale);
/* Allow for maximum size of NUMBER. */
if (precision == 0) precision = 40;
/* Also allow for decimal point and
possible sign. */
/* convert NUMBER datatype to FLOAT if scale > 0,
INT otherwise. */
if (scale > 0)
select_dp->L[i] = sizeof(float);
else
select_dp->L[i] = sizeof(int);
break;
case 8 : /* LONG datatype */
select_dp->L[i] = 240;
break;
case 11 : /* ROWID datatype */
select_dp->L[i] = 18;
break;
case 12 : /* DATE datatype */
select_dp->L[i] = 9;
break;
case 23 : /* RAW datatype */
break;
case 24 : /* LONG RAW datatype */
select_dp->L[i] = 240;
break;
}
/* Allocate space for the select-list data values.
SQLSQLDAAlloc() reserves a pointer location for
V[i] but does not allocate the full space for
the pointer. */
if (select_dp->T[i] != 2)
select_dp->V[i] = (char *) realloc(select_dp->V[i],
select_dp->L[i] + 1);
else
select_dp->V[i] = (char *) realloc(select_dp->V[i],
select_dp->L[i]);
/* Print column headings, right-justifying number
column headings. */
if (select_dp->T[i] == 2)
if (scale > 0)
printf ("%.*s ",select_dp->L[i]+3, select_dp->S[i]);
else
printf ("%.*s ", select_dp->L[i], select_dp->S[i]);
else
printf ("%-.*s ", select_dp->L[i], select_dp->S[i]);
/* Coerce ALL datatypes except for LONG RAW and NUMBER to
character. */
if (select_dp->T[i] != 24 && select_dp->T[i] != 2)
select_dp->T[i] = 1;
/* Coerce the datatypes of NUMBERs to float
or int depending on the scale. */
if (select_dp->T[i] == 2)
if (scale > 0)
select_dp->T[i] = 4; /* float */
else
select_dp->T[i] = 3; /* int */
}
printf ("\n\n");
/* FETCH each row selected and print the column values. */
EXEC SQL WHENEVER NOT FOUND GOTO end_select_loop;
for (;;)
{
EXEC SQL FETCH C USING DESCRIPTOR select_dp;
/* Since each variable returned has been coerced to a
character string, int, or float very little processing
is required here. This routine just prints out the
values on the terminal. */
for (i = 0; i < select_dp->F; i++)
{
if (*select_dp->I[i] < 0)
if (select_dp->T[i] == 4)
printf ("%-*c ",(int)select_dp->L[i]+3, ' ');
else
printf ("%-*c ",(int)select_dp->L[i], ' ');
else
if (select_dp->T[i] == 3) /* int datatype */
printf ("%*d ", (int)select_dp->L[i],
*(int *)select_dp->V[i]);
else if (select_dp->T[i] == 4)/* float datatype*/
printf ("%*.2f ", (int)select_dp->L[i],
*(float *)select_dp->V[i]);
else /* character string */
printf ("%-*s ",
(int)select_dp->L[i], select_dp->V[i]);
}
printf ("\n");
}
end_select_loop:
return;
}
help()
{
puts("\n\nEnter a SQL statement or a PL/SQL block");
puts("at the SQL> prompt.");
puts("Statements can be continued over several");
puts("lines, except within string literals.");
puts("Terminate a SQL statement with a semicolon.");
puts("Terminate a PL/SQL block");
puts("(which can contain embedded semicolons)");
puts("with a slash (/).");
puts("Typing \"exit\" (no semicolon needed)");
puts("exits the program.");
puts("You typed \"?\" or \"help\"");
puts(" to get this message.\n\n");
}
sql_error()
{
int i;
/* ORACLE error handler */
printf ("\n\n%.70s\n",sqlca.sqlerrm.sqlerrmc);
if (parse_flag)
printf("Parse error at character offset %d.\n",
sqlca.sqlerrd[4]);
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLERROR CONTINUE;
EXEC SQL ROLLBACK WORK;
longjmp(jmp_continue, 1);
}
|
Copyright © 1997 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|