Release 1.4.0
A53707_01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts Guide Release 1.4.0 A53707_01 |
|
Oracle Enterprise Manager is a system management tool which provides an integrated solution for managing your heterogeneous environment. It combines a graphical console, agents, common services, and tools to provide an integrated, comprehensive systems management platform for managing Oracle products.
From the Oracle Enterprise Manager's Console, you can:
This chapter presents an overview of the Oracle Enterprise Manager's benefits and major components.
| Topic | See Page |
|---|---|
This section discusses the major benefits of the Oracle Enterprise Manager. The topics are listed below.
| Topic | See Page |
|---|---|
You can manage your distributed systems and databases from the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console.
The Console gives you a central point of control for the Oracle environment through an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) that provides drag-and-drop system management. The interface enables you to be effective with minimal training.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager enables you to manage a heterogeneous environment as easily as a homogeneous one. You can schedule jobs on multiple nodes simultaneously or monitor groups of services together.
Designed to provide the flexibility and customization required by administrators of rapidly growing distributed environments, the Oracle Enterprise Manager easily scales upwards to maintain performance and automate routine tasks. Even in a large system you can customize the Console GUI to display any part of the system.
In a large, distributed database environment, the proportion of nodes per administrator increases rapidly, requiring tools that can automate tasks.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager offers "lights out" (automated) management and proactive event management.
Using the Job Scheduling system, you can automate routine tasks such as database backups or running reports on a regular basis. The Job Scheduling System can schedule and run jobs on remote sites, providing the kind of "lights out" management that is vital in a large, distributed environment.
Using the Event Management system, you can remotely monitor for critical database and system events. You define the events of interest. When one of these events is detected, it is represented graphically on the Console. In addition, you can choose to be notified through electronic mail or page.
To further automate problem detection and correction, Oracle Enterprise Manager can be specified to perform tasks in response to an event. For example, you can register an event to monitor the space usage of a tablespace and, if necessary, run a fix-it job to allocate a new datafile to the tablespace.
Proactive management of an event ensures that a problem is corrected before it noticeably impacts end-users.
See Chapter 3, "Job and Event Systems" for more information on jobs and event sets. For detailed information, refer to Chapter 4, "Job Scheduling," and Chapter 5, "Event Management," of the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide.
You can localize DBA task execution, so that tasks are completed even when a crucial part of the network is down. Localized tasks are dependable since all job processing is performed by the agent.
For example, if you schedule a job on a node, the job will be executed locally at the specified time. Since it is executed locally, the job will run even if a network outage occurs between the node and the Console. The messages are saved until they can be delivered, even if a network connection is down.
For information on the Intelligent Agents, refer to Chapter 6, "Agents and Communication Daemon," of the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide.
Oracle Enterprise Manager's Security System provides easy-to-use administrator level security.
Each administrator's privileges are stored in a credentials file and used by the Oracle Enterprise Manager to manage your connections. When you connect to a database from the Console, your credentials are transparently passed on by Oracle Enterprise Manager; therefore, you do not have to log in repeatedly.
The security management is flexible enough so that you can change it to suit the security roles and policies of the system. You can store a list of your preferred credentials for the nodes and services throughout the network. Because a separate list is stored for each administrator, you can share credentials or have unique ones.
The client/server architecture consists of a centralized console, common services and intelligent agents running on the managed nodes. Various applications reside on top of the common services, performing comprehensive system management tasks.
This section describes the following components of Oracle Enterprise Manager.
| Topic | See Page |
|---|---|
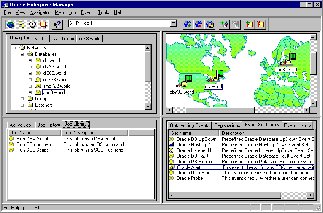
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Console is a graphical user interface that provides menus, toolbars, launch palettes, and the framework to allow access to Oracle tools, plus utilities available through other vendors. The format of the Console screen and the applications displayed are determined by the products purchased and user preferences. See Figure 1-1, "Oracle Enterprise Manager Console" for an illustration of a Console screen.
The windows provide the Navigator, Map, Job, and Event systems. The Navigator discovers and displays a tree list of all the objects in a network, providing a direct view of objects such as user-defined groups, nodes, listeners, names servers, and databases, plus the objects that they contain. The Navigator shows all the network objects with their relationships to other objects.
The Map system allows you to monitor network objects at a glance. With the Map system, you can create, save, modify, and recall views of the network. You simply drag and drop objects from the Navigator into the Map view to create the various groups that you want to monitor.
The Console menu bar provides access to the Navigator, Map, Job, Event, and database administration (DBA) applications. You can also use toolbars and tool palettes to access the tools.
See Chapter 2, "The Console" for descriptions of the basic components and how they are organized. For information on the Console menus, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide, chapter 1.
Oracle Enterprise Manager has a set of common services that help you manage nodes throughout your network.
This section describes the Oracle Enterprise Manager common services.
| Topic | See Page |
|---|---|
The Job Scheduling System allows you to manage job scheduling among the databases, listeners, and nodes that you are administering.
With the Job Scheduling System, you can schedule and run jobs on remote sites throughout the network. Jobs can be scheduled at various times, such as daily or weekly, and at single or multiple destinations.
For example, you can schedule a report to be run every Sunday night on a predetermined set of databases. You only have to schedule the job once; Oracle Enterprise Manager ensures that the job is run on schedule on all specified databases, and it also keeps a history of the job and record of the job's status.
The Event Management System allows you to track and display the status of events occurring on the databases, listeners, and nodes in your network system.
To further automate problem detection and correction, you can also create a fixit job that you specify to be run in response to a particular event.
See Chapter 3, "Job and Event Systems" for information on how these systems execute jobs and monitor events. For information on the Job and Event menus, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide, Chapters 4 and 5.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager repository is a set of tables in an Oracle database. Each administrator is associated with a specific repository in a database. Any information related to the tasks performed by the administrator is stored in that repository.
The repository provides a centralized location for storing information about the state of the environment managed by Oracle Enterprise Manager from the perspective of each console user. It contains information on configurations, jobs and events, historical collections, tuning recommendations, the preferred credentials for each user, and other information associated with each Enterprise Manager Console login.
The repository tables can be installed in any database accessible to the Console. An administrator can log on to the repository database from any machine. Also, the repositories for the administrators do not have to be in the same database.
Enterprise Manager uses Intelligent Agents and a communication daemon to manage Console tasks such as scheduling and running remote jobs, and monitoring events on remote sites.
The Intelligent Agent is a process that runs on remote nodes in the network. Both effective and non-intrusive, it functions as the executor of jobs and events sent by the console via the communication daemon. High availability is ensured since the agent can function regardless of the status of the Console or network connections.
The Intelligent Agent can also be used to discover services on the node where it resides. The Console communication daemon communicates with the Intelligent Agents on the remote nodes in the system.
For information on the Intelligent Agents, refer to Chapter 6, "Agents and Communication Daemon," in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide.
The communication daemon and agent are components responsible for discovering services in the Net8 Assistant network that are used to populate the Navigator tree.
The manner in which the services are located depends on the version of the Intelligent Agent that is on the node that you want to discover.
For information on the communication daemon, refer to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide. For information on using Oracle Network Manager, see the Oracle Network Manager Administrator's Guide. For information on Oracle Enterprise Manager configuration files, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Guide.
Access to Oracle Services on the network is controlled by a set of user-defined, preferred credentials for the available nodes and services. Enterprise Manager encrypts the user authentication information in the repository and provides it as part of the connection request from the Enterprise Manager console or console launched applications.
Oracle Enterprise Manager includes a set of standard integrated database administration applications. These applications are specialized management tools that can be launched directly from the Console or the Administration Toolbar.
For an overview of the database tools, refer to Chapter 4 of this manual or to Chapter 7, "Overview of the Database Tools," in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide.
Third-parties can also write applications that integrate into the Console and use the available common services. These applications can be launched directly from the Console.
A command line interface is sometimes necessary or desirable. Oracle Server Manager provides a conversational line mode. In line mode, you can explicitly execute database administration (DBA) commands on a command line.
For more information about using Server Manager in line mode, refer to Appendix A of the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide.
Enterprise Manager uses the Microsoft Windows online help system to provide you with help information for windows and dialog boxes in the Console and database tools. The Help system is context sensitive, but you can also search through the online help contents or index to find a particular topic.
For information on the Help menu, refer to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide, chapter 1.