Release 2.0
A54630-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8(TM)
ConText(R) Cartridge Application Developer's Guide Release 2.0 A54630-01 |
|
This chapter describes how to view highlighted text using the PL/SQL procedures provided by ConText.
The topics covered in this chapter are:
CTX_QUERY.HIGHLIGHT is a PL/SQL procedure provided by ConText to create various forms of the documents that can be used in an application to produce viewable output.
Other stored procedures in the CTX_QUERY package provide for managing the result tables used to store the viewing output.
The PL/SQL procedure CTX_QUERY.HIGHLIGHTgenerates filtered text, marked-up highlight text, and highlight information. You typically call CTX_QUERY.HIGHLIGHT after executing a text query.
Use CTX_QUERY.HIGHLIGHT to generate the following output for a document:
The positions and lengths of the query terms are specified as offsets from the beginning of the ASCII text version of the document.
| See
Also::
For more information about the structure of the highlight output tables, see "Highlight Table Structures" in Appendix A. For more information about the Windows 32-bit viewer, see "Viewing in Windows" in this chapter. |
The markup that is used to indicate the start and end of a highlighted word or phrase can be specified when CTX_QUERY.HIGHLIGHT is called for a document.
If no markup is specified, HIGHLIGHT uses default markup. The default highlighting mark-up produced by HIGHLIGHT differs depending on the format of the source document.
If the source document is an ASCII document or a formatted document, the default highlighting markup is three angle brackets immediately to the left (<<<) and right (>>>) of each term.
If the source document is an HTML document filtered through an external filter, the default highlighting markup is the same as the highlighting markup for ASCII or formatted documents (<<< and >>>).
If the source document is an HTML document filtered through the internal HTML filter, the default highlighting markup is the HTML tags used to indicate the start and end of a font change:
| See
Also:
For more information about internal and external filters, see Oracle8 ConText Cartridge Administrator's Guide. |
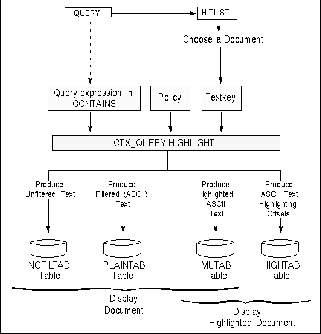
To provide document and highlight viewing in an application, you perform the following tasks:
The result tables required by the HIGHLIGHT procedure can be allocated manually using the CREATE TABLE command in SQL or using the CTX_QUERY.GETTAB procedure.
| See
Also:
For more information about the structure of the highlight output tables, see "Highlight Table Structures" in Appendix A. |
A one-step, two-step, or in-memory query is performed to return a hitlist of documents. The hitlist provides the textkeys that are used to generate highlight and display output for specified documents in the hitlist.
The application passes to CTX_QUERY.HIGHLIGHT a pointer to a document (generally the textkey obtained from the hitlist) and a query expression.
CTX_QUERY. HIGHLIGHT returns to the application various forms of the specified document that can be further processed or displayed by the application.
The highlight offset information and marked-up ASCII text are generated using the query expression specified in the HIGHLIGHT procedure. In addition, the offset information is based on the ASCII text version of the document.
Use the highlight table to manually mark up documents within the application or to display the documents returned by the HIGHLIGHT procedure.
After documents have been processed by the HIGHLIGHT procedure and displayed to the user, drop the highlight result tables.
If the tables were allocated using CTX_QUERY.GETTAB, you use CTX_QUERY.RELTAB to release the tables.
If the tables were created manually, drop the tables using the SQL command DROP TABLE.
In the following code sample, a table called MU_TEXT is created to receive marked-up documents. The CTX_QUERY.HIGHLIGHT procedure is then used to locate specific text in the documents and display the marked-up documents. The text to be searched for and marked up is the same.
To use the code sample, do the following:
create table mu_text (id number, document long);
set termout off
set verify off
col ct new_value ct
col sess new_value sess
col score format 990 head 'RANK'
col textkey format a4 head 'KEY'
col document format a45 word_wrap
set long 60
/* Since this application uses a shared results table */
/* for the hitlist, the application must create a */
/* unique id for each user sharing the results table. */
/* In this example, the unique id is created from the */
/* "sessionid" parameter of the users environment. */
select userenv('sessionid') sess from dual;
/* Run an initial text query to return a hitlist */
begin ctx_query.contains
('EMP_HISTORY','&1','CTX_TEMP',1,&sess);
end;
/* Count the hits */
select count(*) ct from EMP,CTX_TEMP
where empno=textkey
and conid=&sess;
/* Clear prior results from MU_TEXT */
delete MU_TEXT;
commit;
declare
tk varchar2(12)
numtk number(10);
mudoc varchar2(2000);
cursor s is
select textkey from CTX_TEMP,EMP
where empno=textkey
and conid=&sess;
begin
open s;
/*for each hit, produce a marked up row*/
for i in 1 ..&ct loop
fetch s into tk;
/*create numeric id for MU_TEXT from textkey*/
numtk := to_number(tk);
/* call ctx_query.highlight for each document using */
/* the same policy and query expression from the */
/* initial query. Create marked-up ASCII output for */
/* document, stored in mutab table named MU_TEXT. */
begin
ctx_query.highlight(
cspec => 'EMP_HISTORY',
textkey => tk,
query => '&1',
id => numtk,
mutab => 'MU_TEXT');
end;
end loop;
end;
/*Join the hits with the marked-up docs*/
select score RANK, textkey KEY, document
from CTX_TEMP, MU_TEXT
where id=to_number(textkey)
and conid=&sess
order by score desc;
set echo on
In the following example, the sample code has been stored as a script named highlight.sql and the query term is the word used:
@highlight 'used'
The output generated by HIGHLIGHT.SQL is:
RANK KEY DOCUMENT
-------------------
10 7369 <<<Used>>> to build horse shoes
10 7698 Blake <<<used>>> to be a manager at apple
The query term used was found in two documents (textkeys 7369 and 7698). CTX_QUERY.HIGHLIGHT highlighted the specified term using the default markup '<<<' and '>>>'.
You can use the Oracle8 ConText Cartridge Viewer Control (CTXV32.OCX) to allow users to view highlighted documents in a Windows 32-bit environment. The viewer enables the user to browse documents in the supported formats with query terms highlighted.
You embed the control in client-side applications. To operate the viewer, you need not write any PL/SQL code; given the database connection, the document textkey, and the query term, the viewer control displays the document with highlights.
The user can view a Word document, for example, as it would appear in Microsoft Word. The user can also scroll through the document using the Next and Previous buttons to jump to the next or previous occurrence of the search term(s).
As OCX modules are not stand-alone executables, you need a development environment such as Visual C++ or Visual Basic to exploit the functionality of the ConText Viewer Control. Within such an environment, you can add the control to the tool palette, from where you can place instances of the control on a form or canvas.
For example, in Visual Basic 4.0, you add the control to the tool palette by selecting Custom Controls from the Tool menu. Use the browser to select the Oracle8 ConText Viewer Control, CTXV32.OCX, from the oracle_home\BIN directory.
Alternatively, you can create instances of the control dynamically, using the identification string "CTXV32.CTXViewer.1"
If the viewer control is embedded in an HTML page, the browser must support ActiveX components and the client machine must have the viewer installed on it with all required support files. The viewer uses SQL*Net to communicate with the database. Within HTML, you can invoke the methods using Visual Basic scripting, for example, and change properties with the OBJECT tag and parameter settings syntax.
You can use the ConText Cartridge Viewer Control to view documents in the following server-side supported formats:
If you are not using the OCX to view documents in 32-bit Windows environment, you can use the ConText I/O utility (CTXIO32) to move documents (highlighted or not) from database tables to the client operating system and vice-versa. Documents dowloaded to the client operating system can be viewed in their native applications.
| See
Also:
For more information about the 32-bit Windows I/O utility, see Appendix D, "Input/Output Utility". |
|
Copyright © 1997 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|